Planets Distance From The Sun In Au
Kalali
Mar 24, 2025 · 6 min read
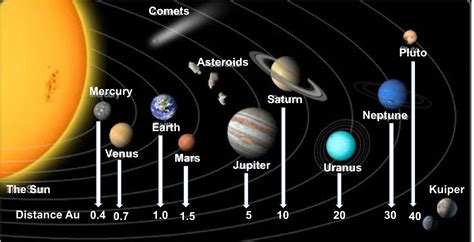
Table of Contents
Planets' Distance from the Sun in AU: A Comprehensive Guide
The vast expanse of our solar system is often difficult to comprehend. Understanding the distances between celestial bodies, particularly the planets and the Sun, is crucial to grasping the scale and dynamics of our cosmic neighborhood. This guide dives deep into planetary distances from the Sun, primarily using the astronomical unit (AU) as our measuring stick. We'll explore the concept of AU, examine the distances of each planet, delve into the reasons for varying distances, and touch upon the implications of these distances for planetary characteristics and habitability.
What is an Astronomical Unit (AU)?
Before we delve into the distances, let's define our unit of measurement: the astronomical unit (AU). An AU is the average distance between the Earth and the Sun. It's approximately 149.6 million kilometers (93 million miles). Using AU simplifies expressing the vast distances within our solar system, making them easier to comprehend and compare. Instead of dealing with incredibly large numbers in kilometers or miles, we can use a more manageable scale based on the Earth-Sun distance.
Planetary Distances in AU: A Detailed Look
The following table summarizes the average distance of each planet from the Sun in AU. Remember that planetary orbits are elliptical, not perfectly circular, so these are average distances.
| Planet | Average Distance from Sun (AU) | Perihelion (AU) | Aphelion (AU) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mercury | 0.39 | 0.31 | 0.47 |
| Venus | 0.72 | 0.72 | 0.73 |
| Earth | 1.00 | 0.98 | 1.02 |
| Mars | 1.52 | 1.38 | 1.67 |
| Jupiter | 5.20 | 4.95 | 5.46 |
| Saturn | 9.54 | 9.04 | 10.05 |
| Uranus | 19.20 | 18.36 | 20.09 |
| Neptune | 30.07 | 29.77 | 30.36 |
Note: Perihelion is the point in a planet's orbit where it's closest to the Sun, and aphelion is the point where it's farthest.
Mercury: The Innermost Planet
Mercury, at a mere 0.39 AU from the Sun, experiences extreme temperature variations. Its proximity to the Sun results in scorching daytime temperatures and frigid nighttime temperatures, due to the lack of a significant atmosphere to regulate temperature.
Venus: The Hottest Planet
Venus orbits the Sun at an average distance of 0.72 AU. Despite being farther from the Sun than Mercury, it's the hottest planet in our solar system. This is due to its incredibly dense atmosphere, which traps heat through a runaway greenhouse effect.
Earth: Our Habitable Home
Earth, at 1 AU from the Sun, is situated within the habitable zone—the region around a star where liquid water can exist on a planet's surface. This distance plays a crucial role in supporting life as we know it.
Mars: The Red Planet
Mars, located at 1.52 AU from the Sun, receives significantly less solar radiation than Earth. Its thin atmosphere contributes to large temperature variations and makes it a much colder and less hospitable environment.
The Gas Giants: Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune
The outer planets – Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune – are gas giants with vastly different characteristics. Their distances from the Sun are significantly greater than the terrestrial planets.
- Jupiter (5.20 AU): The largest planet in our solar system, Jupiter has a powerful magnetic field and many moons.
- Saturn (9.54 AU): Famous for its stunning rings, Saturn is another gas giant with a complex system of moons and atmospheric phenomena.
- Uranus (19.20 AU): An ice giant, Uranus has a unique axial tilt, almost lying on its side.
- Neptune (30.07 AU): The farthest planet from the Sun, Neptune experiences extremely low temperatures and has a strong wind system.
Why Do Planetary Distances Vary?
The varying distances of planets from the Sun are a result of the process of planetary formation within the early solar system. The solar system formed from a rotating cloud of gas and dust called the solar nebula. As the nebula collapsed, it formed a spinning disk with the Sun at the center. Planets formed from the accretion of dust and gas within this disk.
The initial distribution of matter within the disk, along with gravitational interactions between the forming planets and the Sun, determined their final orbital distances. The inner, rocky planets formed closer to the Sun where temperatures were higher, while the outer, gas giants formed farther out where temperatures were cooler, allowing for the accumulation of lighter elements like hydrogen and helium. Gravitational interactions between the planets during their formation also played a significant role in shaping their orbits and final distances.
Implications of Planetary Distance for Habitability
Planetary distance from its star is a major factor in determining a planet's habitability. The distance influences the amount of stellar radiation received by the planet, which, in turn, affects its temperature, atmospheric composition, and the presence of liquid water—all critical factors for life as we know it.
The habitable zone, also known as the Goldilocks zone, is the region around a star where the temperature is just right for liquid water to exist on a planet's surface. This zone is not a fixed distance but depends on the star's luminosity and temperature. A hotter star will have a wider habitable zone, while a cooler star will have a narrower one.
Earth's position within the Sun's habitable zone is a key reason why it can support life. Planets too close to their stars may experience runaway greenhouse effects, while planets too far may be frozen and uninhabitable.
Exploring Beyond Our Solar System: Exoplanet Distances
The concept of AU extends beyond our solar system. Astronomers use AU to describe the distances of exoplanets (planets orbiting other stars) from their host stars. While the AU remains a useful unit, for exoplanets orbiting distant stars, larger units like light-years or parsecs are more practical.
Future Discoveries and Refinements
Our understanding of planetary distances is constantly evolving. As technology advances, we can make more precise measurements of planetary orbits and refine our knowledge of their distances from the Sun. Future missions and observations might reveal subtle details about planetary movements and refine our understanding of the dynamics of our solar system and beyond.
Conclusion: A Cosmic Perspective on Distance
Understanding planetary distances from the Sun in AU provides a crucial framework for comprehending the scale and structure of our solar system. It helps us appreciate the diverse conditions found on different planets and the profound influence of distance on planetary characteristics and habitability. By grasping these concepts, we gain a deeper appreciation for the unique position of Earth within our cosmic neighborhood and the incredible complexity of the solar system we call home. The journey to fully understand the distances and the implications of these distances within our solar system and beyond is an ongoing one, and future discoveries promise to further enrich our understanding of the cosmos.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Cuanto Es 7 Pies En Metros
Mar 29, 2025
-
5 L Equals How Many Ml
Mar 29, 2025
-
How Many Gallons Is 16 Cups
Mar 29, 2025
-
What Is 4 20 As A Percent
Mar 29, 2025
-
What Is The Function Of The Ventral Hypothalamic Neurons
Mar 29, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Planets Distance From The Sun In Au . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
