State Of Each Triangle Is Acute Obtuse Or Right
Kalali
Mar 23, 2025 · 5 min read
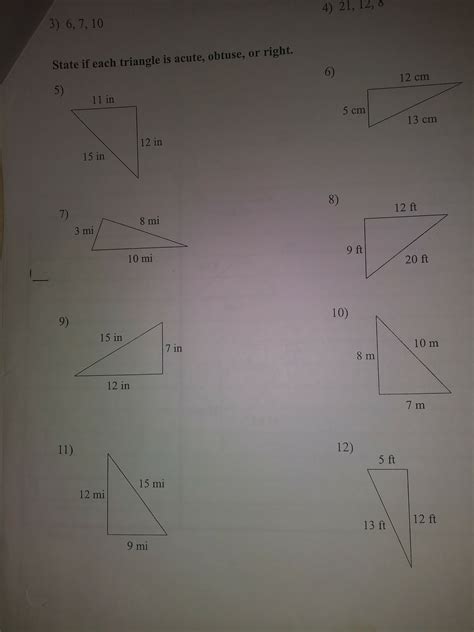
Table of Contents
Determining if a Triangle is Acute, Obtuse, or Right: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding the properties of triangles is fundamental in geometry. One crucial aspect is classifying triangles based on their angles: acute, obtuse, or right. This article provides a comprehensive guide to identifying the state of a triangle, covering various methods, including using angle measurements, side lengths, and the Pythagorean theorem. We'll delve into practical examples and explore the underlying mathematical principles. By the end, you'll be confidently classifying triangles based on their angles.
Understanding Triangle Angle Classification
Triangles are classified based on their angles into three categories:
- Acute Triangle: A triangle where all three angles are less than 90 degrees (acute angles).
- Obtuse Triangle: A triangle with one angle greater than 90 degrees (obtuse angle). Note that it can only have one obtuse angle.
- Right Triangle: A triangle containing one 90-degree angle (right angle).
Method 1: Using Angle Measurements
The most straightforward method for classifying a triangle is by directly measuring its angles. If you have the angle measurements, simply check which category they fall into:
- Acute: All angles < 90°
- Obtuse: One angle > 90°
- Right: One angle = 90°
Example:
A triangle has angles measuring 60°, 60°, and 60°. Since all angles are less than 90°, this is an acute triangle.
Another triangle has angles measuring 30°, 60°, and 90°. The presence of a 90° angle makes this a right triangle.
Finally, a triangle with angles 20°, 110°, and 50° is an obtuse triangle due to the 110° angle.
Method 2: Using Side Lengths and the Pythagorean Theorem
When angle measurements aren't directly available, you can determine the triangle's type using its side lengths and the Pythagorean theorem. This method is particularly useful for right triangles.
The Pythagorean theorem states that in a right-angled triangle, the square of the hypotenuse (the longest side) is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides (legs). Mathematically:
a² + b² = c²
where 'a' and 'b' are the lengths of the legs, and 'c' is the length of the hypotenuse.
Determining if a Triangle is a Right Triangle:
If the squares of the two shorter sides add up to the square of the longest side, then it's a right triangle. If not, it's either acute or obtuse.
Determining if a Triangle is Acute or Obtuse:
For triangles that are not right-angled, we use a modified version of the Pythagorean theorem:
-
Acute Triangle: a² + b² > c² (The sum of the squares of the two shorter sides is greater than the square of the longest side).
-
Obtuse Triangle: a² + b² < c² (The sum of the squares of the two shorter sides is less than the square of the longest side).
Examples:
-
Triangle 1: Sides of length 3, 4, and 5. 3² + 4² = 9 + 16 = 25 5² = 25 Since 3² + 4² = 5², this is a right triangle.
-
Triangle 2: Sides of length 2, 3, and 4. 2² + 3² = 4 + 9 = 13 4² = 16 Since 2² + 3² < 4², this is an obtuse triangle.
-
Triangle 3: Sides of length 5, 12, and 13. 5² + 12² = 25 + 144 = 169 13² = 169 Since 5² + 12² = 13², this is a right triangle.
-
Triangle 4: Sides of length 6, 8, and 9. 6² + 8² = 36 + 64 = 100 9² = 81 Since 6² + 8² > 9², this is an acute triangle.
Visualizing Triangle Classification
Understanding the relationship between angles and sides is crucial. Imagine starting with a right triangle. If you slightly increase the angle opposite the hypotenuse, it becomes obtuse, and the hypotenuse length increases accordingly. Conversely, decreasing that angle results in an acute triangle with a shorter hypotenuse.
Advanced Techniques and Considerations
While the methods described above are sufficient for most cases, some situations require more advanced techniques:
-
Using Trigonometry: Trigonometric functions like sine, cosine, and tangent can be applied to determine angles in triangles, particularly when dealing with problems involving specific angles or ratios.
-
Law of Cosines: This law can be used to find the length of a side or an angle in a triangle when you know the lengths of the other two sides and the angle between them. It's particularly useful for non-right-angled triangles.
-
Law of Sines: This law relates the lengths of the sides of a triangle to the sines of its angles. It’s useful when you have information about angles and sides in a non-right-angled triangle.
Practical Applications
The ability to classify triangles is important in various fields, including:
-
Engineering: Understanding triangle types is essential in structural design, ensuring stability and strength.
-
Architecture: Classifying triangles helps in designing stable and aesthetically pleasing structures.
-
Computer Graphics: Triangle classification is crucial in computer graphics for rendering and 3D modeling.
-
Cartography: Understanding triangles is important in mapmaking and surveying.
Troubleshooting Common Mistakes
-
Incorrect identification of the hypotenuse: Always ensure you've correctly identified the longest side (hypotenuse) when using the Pythagorean theorem.
-
Miscalculation of squares: Double-check your calculations when squaring side lengths. A small error can lead to an incorrect classification.
-
Not considering all angles: When using angle measurements, remember to consider all three angles to ensure accuracy. For example, a triangle may appear obtuse but might have three angles in total that are less than 180 degrees.
Conclusion
Classifying triangles as acute, obtuse, or right is a fundamental concept in geometry with wide-ranging applications. This comprehensive guide has presented various methods, from direct angle measurement to the utilization of the Pythagorean theorem and its extensions. By understanding these principles and practicing with various examples, you can confidently determine the type of any given triangle. Remember to double-check your calculations and carefully consider the relationships between angles and sides to ensure accurate classification. Mastering this skill enhances your problem-solving abilities in various mathematical and real-world contexts.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Ft Is 118 Inches
Mar 24, 2025
-
How Many Inches Is 240 Cm
Mar 24, 2025
-
What Is A 13 Out Of 16
Mar 24, 2025
-
How Many Valence Electrons Does Ar Have
Mar 24, 2025
-
How Many Centimeters In 40 Inches
Mar 24, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about State Of Each Triangle Is Acute Obtuse Or Right . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
