This Is A Passageway For Blood Vessels And Nerves
Kalali
Mar 31, 2025 · 7 min read
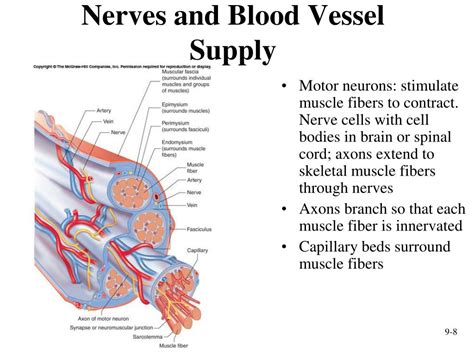
Table of Contents
This Is a Passageway for Blood Vessels and Nerves: Exploring Fascial Planes and Their Clinical Significance
The human body is a marvel of intricate design, a complex network of interconnected systems working in harmony. Within this intricate tapestry lies a often-overlooked yet crucial component: the fascial planes. These are the passageways for blood vessels and nerves, providing essential pathways for communication and sustenance throughout the body. Understanding their structure, function, and clinical significance is vital for healthcare professionals and anyone interested in the intricacies of human anatomy and physiology.
What are Fascial Planes?
Fascial planes are potential spaces between adjacent layers of fascia. Fascia, a ubiquitous connective tissue, is not a single structure but a complex, three-dimensional network composed of various layers with different densities and compositions. It forms a continuous sheet throughout the body, wrapping around muscles, organs, and other structures. These layers aren't tightly adhered to each other, but rather separated by potential spaces—the fascial planes. These spaces allow for the passage of blood vessels, nerves, and lymphatics, facilitating the transmission of signals and the supply of nutrients and oxygen to various tissues.
The Composition of Fascial Planes
Fascial planes aren't simply empty spaces; they contain a small amount of loose connective tissue, adipose tissue (fat), and interstitial fluid. This loose composition allows for the gliding and sliding movement between adjacent structures, crucial for joint mobility and preventing friction. The specific components within a fascial plane vary depending on its location in the body.
The Significance of the Loose Connective Tissue
The loose connective tissue within the fascial planes plays a vital role in cushioning and protecting the delicate blood vessels and nerves passing through them. This cushioning effect minimizes the risk of damage during movement or external forces. Furthermore, this tissue helps to distribute forces evenly across the body, preventing undue stress on individual structures.
The Role of Fascial Planes in Blood Vessel and Nerve Passage
The fascial planes act as natural conduits for the circulatory and nervous systems. Arteries, veins, and nerves often follow these pathways, minimizing the risk of damage and maximizing efficiency. The arrangement of these structures within the fascial planes is crucial for the proper function of the entire body.
Blood Vessel Passage
Blood vessels, including arteries and veins, traverse fascial planes to reach various tissues and organs. Arteries deliver oxygenated blood, while veins carry deoxygenated blood back to the heart. The arrangement of these vessels within the fascial planes ensures efficient delivery and removal of blood, providing the necessary nutrients and oxygen for cellular function and waste removal. Disruptions in these pathways can lead to compromised blood flow, resulting in ischemia (reduced blood supply) or other complications.
Nerve Passage
Nerves, crucial for communication between the brain and the rest of the body, also travel through fascial planes. These planes protect nerves from damage, allowing them to transmit sensory information and motor commands efficiently. The fascial planes provide a protective sheath, preventing compression or stretching that could impair nerve function. Damage to the fascial planes can result in nerve compression, leading to pain, numbness, or weakness.
Clinical Significance of Fascial Planes
Understanding fascial planes is crucial in various clinical settings. Knowledge of their anatomy and physiology is essential for surgeons, physical therapists, and other healthcare professionals.
Surgery
Surgical procedures often involve navigating through fascial planes to access specific structures while minimizing damage to surrounding tissues. Surgeons must possess a detailed understanding of fascial plane anatomy to perform minimally invasive procedures and reduce post-operative complications. Dissecting along fascial planes reduces trauma, bleeding, and the risk of injuring nerves and blood vessels.
Pain Management
Many musculoskeletal pain conditions are associated with dysfunction within fascial planes. Restrictions or adhesions in these planes can lead to pain, reduced mobility, and other functional limitations. Manual therapies, such as massage and myofascial release, aim to address these restrictions, restoring normal gliding and sliding movement between fascial layers and relieving pain. By understanding the anatomical pathways of nerves within the fascial planes, healthcare professionals can more effectively target pain generation and improve patient outcomes.
Physical Therapy
Physical therapists utilize their knowledge of fascial planes to design effective rehabilitation programs for patients recovering from injuries or surgeries. Manual techniques and therapeutic exercises aim to restore normal fascial gliding, improve joint mobility, and reduce pain. The focus on fascial planes in physical therapy emphasizes the interconnected nature of the body and highlights the importance of addressing fascial restrictions for optimal recovery.
Oncology
Cancer cells can invade and spread through fascial planes, making it crucial for oncologists to understand these pathways during cancer diagnosis and treatment planning. Knowledge of fascial planes assists in determining the extent of cancer spread (staging), guiding surgical resection, and planning radiotherapy treatments.
Fascial Plane Dysfunction and Associated Conditions
Disruptions in the normal function of fascial planes can lead to a range of conditions, including:
- Chronic pain: Adhesions and restrictions within fascial planes can cause persistent pain and limited mobility. This pain might be localized or referred to other areas of the body due to nerve involvement.
- Compartment syndrome: This condition occurs when increased pressure within a confined fascial compartment compromises blood supply to the muscles and nerves within that compartment. It's a medical emergency requiring prompt attention.
- Scar tissue formation: After injury or surgery, scar tissue can form within fascial planes, leading to adhesions and restrictions. This can limit mobility and cause pain.
- Joint dysfunction: Restrictions in fascial planes can impair joint movement, contributing to stiffness and decreased range of motion.
- Nerve compression: Adhesions or inflammation within fascial planes can compress nerves, leading to pain, numbness, tingling, or weakness in the affected area. Examples include carpal tunnel syndrome and thoracic outlet syndrome.
- Lymphedema: Obstruction of lymphatic flow within fascial planes can lead to the accumulation of fluid in the tissues, resulting in swelling (edema).
Advanced Imaging Techniques for Visualizing Fascial Planes
Advances in medical imaging have significantly improved our ability to visualize fascial planes and their associated structures. Techniques such as ultrasound, MRI, and CT scans provide detailed images of these planes, allowing for a better understanding of their anatomy and pathology. These imaging techniques are crucial for diagnosing conditions related to fascial plane dysfunction and for guiding minimally invasive procedures.
Ultrasound
Ultrasound imaging uses high-frequency sound waves to create real-time images of soft tissues, including fascial planes. It's a readily available and relatively inexpensive technique, making it valuable for evaluating fascial thickness, texture, and gliding properties.
MRI
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) provides high-resolution images of soft tissues, offering detailed visualization of fascial planes and their relationships with surrounding structures. MRI is particularly useful for identifying abnormalities, such as adhesions or inflammation, within fascial planes.
CT Scans
Computed tomography (CT) scans use X-rays to create cross-sectional images of the body. While not as detailed as MRI for soft tissues, CT scans can be valuable for assessing bony structures and identifying any impingement or compression on fascial planes.
Future Directions in Fascial Plane Research
Research on fascial planes continues to evolve, with ongoing investigations focusing on their role in various physiological processes and pathological conditions. Future research will likely focus on:
- Advanced imaging techniques: Development of more sophisticated imaging techniques will enable even more precise visualization and analysis of fascial planes.
- Biomechanical properties: Further studies are needed to better understand the biomechanical properties of fascial planes and their contribution to overall body mechanics.
- Treatment strategies: Development of new therapeutic interventions, such as targeted drug delivery and regenerative medicine approaches, will aim to address fascial plane dysfunction and improve patient outcomes.
- Interdisciplinary approaches: Continued collaborative efforts between clinicians, researchers, and engineers will be essential to advance our understanding and management of fascial plane-related conditions.
Conclusion
Fascial planes, often overlooked, are crucial passageways for blood vessels and nerves, providing essential pathways for the body's physiological functions. Understanding their anatomy, physiology, and clinical significance is vital for healthcare professionals and researchers alike. As research continues to advance, our understanding of these vital pathways will undoubtedly improve, leading to better diagnosis, treatment, and ultimately, patient outcomes. The intricate network of fascial planes underscores the interconnectedness of the human body, emphasizing the holistic nature of health and disease. By appreciating the significance of these often-unsung structures, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the remarkable complexity and resilience of the human form.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
41 Degrees Celsius Converted To Fahrenheit
Apr 01, 2025
-
Is 0 0000008 J A Little Kinetic Enegy
Apr 01, 2025
-
17 Of 20 Is What Percent
Apr 01, 2025
-
What Is 6 To The Power Of 3
Apr 01, 2025
-
Cual Es El 10 Por Ciento De 1000
Apr 01, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about This Is A Passageway For Blood Vessels And Nerves . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
