What Are The Common Multiples Of 6 And 8
Kalali
Mar 25, 2025 · 4 min read
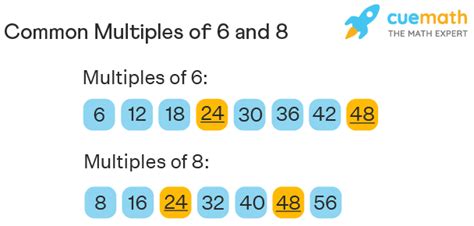
Table of Contents
What Are the Common Multiples of 6 and 8? A Deep Dive into Least Common Multiples (LCM)
Finding common multiples, especially the least common multiple (LCM), is a fundamental concept in mathematics with wide-ranging applications. This comprehensive guide will explore the common multiples of 6 and 8, providing a clear understanding of the process, its significance, and practical examples. We'll delve into various methods for determining the LCM, including listing multiples, prime factorization, and using the greatest common divisor (GCD).
Understanding Multiples
Before we tackle the common multiples of 6 and 8, let's establish a solid understanding of the term "multiple." A multiple of a number is the product of that number and any integer (whole number). For instance:
- Multiples of 6: 6, 12, 18, 24, 30, 36, 42, 48, 54, 60, 66, 72, 78, 84, 90, 96, 102, 108, 114, 120... and so on to infinity.
- Multiples of 8: 8, 16, 24, 32, 40, 48, 56, 64, 72, 80, 88, 96, 104, 112, 120... and so on to infinity.
Identifying Common Multiples
Common multiples are numbers that appear in the lists of multiples for both numbers. Looking at the lists above, we can already spot some common multiples of 6 and 8:
- 24: Appears in both lists.
- 48: Appears in both lists.
- 72: Appears in both lists.
- 96: Appears in both lists.
- 120: Appears in both lists.
And so on. There are infinitely many common multiples of any two whole numbers.
The Least Common Multiple (LCM)
While there are infinitely many common multiples, there's only one least common multiple (LCM). The LCM is the smallest positive number that is a multiple of both numbers. In the case of 6 and 8, the LCM is 24.
Methods for Finding the LCM
Several methods can be used to determine the LCM of two or more numbers. Let's explore the most common approaches:
1. Listing Multiples Method
This method involves listing the multiples of each number until a common multiple is found. As demonstrated above, this works well for smaller numbers but becomes less efficient with larger numbers.
2. Prime Factorization Method
This is a more efficient and systematic approach, especially for larger numbers. It involves:
-
Find the prime factorization of each number:
- 6 = 2 x 3
- 8 = 2 x 2 x 2 = 2³
-
Identify the highest power of each prime factor present in either factorization:
- The prime factors are 2 and 3.
- The highest power of 2 is 2³ = 8.
- The highest power of 3 is 3¹ = 3.
-
Multiply the highest powers together:
- LCM(6, 8) = 2³ x 3 = 8 x 3 = 24
3. Using the Greatest Common Divisor (GCD) Method
The LCM and GCD (Greatest Common Divisor) are related. The product of the LCM and GCD of two numbers is equal to the product of the two numbers. Therefore:
LCM(a, b) = (a x b) / GCD(a, b)
-
Find the GCD of 6 and 8: The GCD is the largest number that divides both 6 and 8 without leaving a remainder. The GCD of 6 and 8 is 2.
-
Apply the formula: LCM(6, 8) = (6 x 8) / 2 = 48 / 2 = 24
Applications of LCM
The concept of the least common multiple has numerous practical applications in various fields:
1. Fraction Operations
Finding the LCM is crucial when adding or subtracting fractions with different denominators. You need to find the LCM of the denominators to create equivalent fractions with a common denominator.
2. Scheduling Problems
Imagine two buses depart from the same station, one every 6 minutes and the other every 8 minutes. The LCM helps determine when both buses will depart simultaneously again. In this case, the LCM(6, 8) = 24, meaning they will depart together again in 24 minutes.
3. Measurement Conversions
When converting between different units of measurement, the LCM can help simplify calculations.
4. Project Management
In project management, LCM can help coordinate tasks with different durations or cycles.
5. Gear Ratios
In mechanics and engineering, understanding LCM is critical for determining gear ratios and synchronized movements in machinery.
Beyond Two Numbers: Finding the LCM of More Than Two Numbers
The methods described above can be extended to find the LCM of more than two numbers. For the prime factorization method, you simply include all prime factors from all numbers, taking the highest power of each. For the GCD method, you can apply it iteratively, finding the LCM of two numbers at a time, and then using the result to find the LCM with the next number, and so on.
Conclusion: Mastering LCM for Mathematical Proficiency
Understanding and calculating the least common multiple is a fundamental skill in mathematics with practical applications in various aspects of life. Whether you're simplifying fractions, solving scheduling problems, or tackling engineering challenges, mastering LCM enhances problem-solving capabilities and provides a deeper understanding of number relationships. The methods outlined in this guide, particularly the prime factorization method, provide efficient ways to determine the LCM for numbers of any size, equipping you with a valuable tool for your mathematical journey. Remember to practice regularly to reinforce your understanding and build confidence in applying these techniques. The more you work with LCM, the more intuitive and effortless the process will become.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is 40 F In Celsius
Mar 27, 2025
-
How Much Is 1 1 2 Cups In Oz
Mar 27, 2025
-
How Much Is 12 Oz Of Water
Mar 27, 2025
-
How Many Feet In 96 Inches
Mar 27, 2025
-
Click On The Beaker That Shows The Bronsted Lowry Base
Mar 27, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Are The Common Multiples Of 6 And 8 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
