What Element Has 6 Protons 7 Neutrons And 6 Electrons
Kalali
Mar 30, 2025 · 5 min read
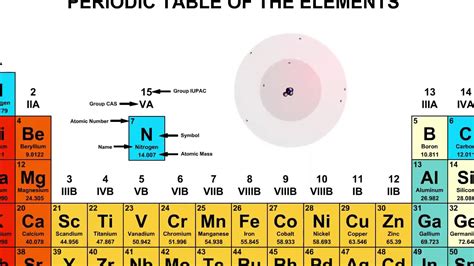
Table of Contents
What Element Has 6 Protons, 7 Neutrons, and 6 Electrons? Unraveling the Mystery of Isotopes
The question, "What element has 6 protons, 7 neutrons, and 6 electrons?" might seem deceptively simple at first glance. However, it delves into the fascinating world of atomic structure and isotopes, requiring a deeper understanding of fundamental chemistry principles. Let's unravel this mystery step-by-step.
Understanding Atomic Structure: Protons, Neutrons, and Electrons
Before we identify the element, let's refresh our understanding of the subatomic particles that constitute an atom:
- Protons: Positively charged particles located in the atom's nucleus. The number of protons defines the atomic number of an element, which uniquely identifies it on the periodic table.
- Neutrons: Neutral particles (no charge) also residing in the nucleus. Neutrons contribute to the atom's mass but not its charge.
- Electrons: Negatively charged particles orbiting the nucleus in electron shells or energy levels. The number of electrons typically equals the number of protons in a neutral atom, ensuring a balanced charge.
Deciphering the Element: The Role of Protons
The key to identifying the element lies in the number of protons. The question states there are 6 protons. This immediately tells us the atomic number of the element is 6. Now, we consult the periodic table. The element with an atomic number of 6 is Carbon (C).
Isotopes: The Significance of Neutrons
While the number of protons identifies the element, the number of neutrons can vary. Atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons are called isotopes. These isotopes have the same atomic number (same number of protons) but different mass numbers (total number of protons and neutrons).
The question specifies 7 neutrons. Since carbon has 6 protons, this isotope has a mass number of 6 (protons) + 7 (neutrons) = 13. Therefore, we are dealing with Carbon-13 (¹³C).
Carbon-13: Properties and Abundance
Carbon-13 is a stable isotope of carbon, meaning it doesn't undergo radioactive decay. It's naturally occurring, although less abundant than the more common isotope, Carbon-12 (¹²C), which has 6 protons and 6 neutrons. Carbon-13 makes up approximately 1.1% of naturally occurring carbon.
Applications of Carbon-13
The properties of Carbon-13 make it useful in several scientific applications:
-
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Spectroscopy: Carbon-13 NMR is a powerful technique used in organic chemistry to determine the structure of molecules. The different chemical environments of carbon atoms in a molecule result in distinct signals in the NMR spectrum, allowing researchers to identify and characterize compounds. This is particularly valuable in drug discovery, material science, and other fields.
-
Radiocarbon Dating (AMS): While ¹⁴C is primarily used in radiocarbon dating, advancements in Accelerator Mass Spectrometry (AMS) allow for more precise dating using smaller samples with ¹³C as a reference. This method improves accuracy and expands the range of materials that can be dated.
-
Metabolic Studies (Stable Isotope Tracing): Scientists use ¹³C-labeled molecules as tracers to study metabolic pathways in organisms. By monitoring the incorporation of the labeled carbon into different molecules, researchers can gain insights into metabolic processes and identify potential health issues. This technique has important implications for understanding nutrition, disease mechanisms, and drug metabolism.
-
Food and Agriculture: Stable isotope analysis, including ¹³C measurements, is used in food science and agriculture to trace the origin of food products, detect adulteration, and study the impact of farming practices on the environment. This helps ensure food quality and safety, as well as promotes sustainable agriculture.
-
Environmental Science: The isotopic composition of carbon in various environmental samples like water, soil, and sediments can provide valuable information about environmental processes, such as photosynthesis, respiration, and carbon cycling. This data helps researchers understand climate change, pollution, and ecosystem dynamics.
Distinguishing Between Ions and Isotopes
It's important to note that the number of electrons can vary, even within the same isotope. If the number of electrons differs from the number of protons, the atom becomes an ion. A positive ion (cation) has more protons than electrons, while a negative ion (anion) has more electrons than protons.
However, the question specifies 6 electrons, matching the number of protons, indicating a neutral atom of Carbon-13. It's crucial to differentiate between isotopes (different numbers of neutrons) and ions (different numbers of electrons) to accurately describe an atom.
The Importance of Isotopes in Chemistry and Beyond
The concept of isotopes is fundamental to many fields of science and technology. Isotopes play a critical role in:
- Nuclear Medicine: Radioactive isotopes are used in various medical imaging techniques and cancer treatments.
- Nuclear Power: Nuclear reactors rely on the controlled fission of specific isotopes to generate electricity.
- Geochronology: Isotopes are used to determine the age of rocks and other geological materials.
- Forensic Science: Isotopic analysis aids in determining the origin and provenance of materials, such as in identifying the source of explosives or tracing the origin of drugs.
Conclusion: Carbon-13, A Stable and Useful Isotope
In conclusion, an element with 6 protons, 7 neutrons, and 6 electrons is Carbon-13 (¹³C), a stable and naturally occurring isotope of carbon. Its unique properties make it invaluable in a wide range of scientific applications, from determining molecular structures to studying metabolic processes and tracing the origin of materials. Understanding the interplay between protons, neutrons, and electrons is crucial in comprehending atomic structure, isotopic variations, and the diverse roles of elements in the world around us. Further exploration into the world of isotopes reveals the richness and complexity of the chemical elements and their importance in diverse scientific and technological fields. The ability to identify and analyze isotopes has profound implications for fields ranging from medicine and environmental science to archaeology and materials science, highlighting the profound significance of basic chemistry principles in a vast array of applications.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Inches Is 128 Cm
Apr 01, 2025
-
Cuanto Es 63 Pulgadas En Pies
Apr 01, 2025
-
What Percentage Is 35 Out Of 50
Apr 01, 2025
-
How To Make A Velocity Vs Time Graph
Apr 01, 2025
-
Is The Atlantic Colder Than The Pacific
Apr 01, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Element Has 6 Protons 7 Neutrons And 6 Electrons . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
