What Is 400 Degrees In Celsius
Kalali
Mar 31, 2025 · 5 min read
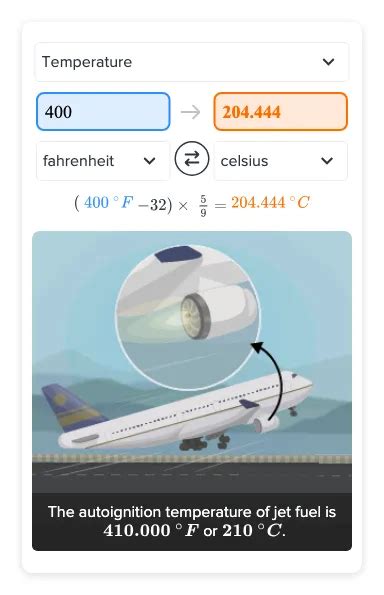
Table of Contents
What is 400 Degrees in Celsius? A Comprehensive Guide
Knowing how to convert temperatures between Celsius and Fahrenheit is a crucial skill, whether you're a chef perfecting a recipe, a scientist conducting an experiment, or simply someone curious about the world around us. This comprehensive guide will delve into the conversion of 400 degrees Fahrenheit to Celsius, exploring the process, its practical applications, and offering a broader understanding of temperature scales.
Understanding Temperature Scales
Before we jump into the conversion, let's quickly review the two most common temperature scales: Celsius and Fahrenheit.
Celsius (°C): This scale, also known as the centigrade scale, is part of the International System of Units (SI) and is widely used globally. It sets the freezing point of water at 0°C and the boiling point at 100°C at standard atmospheric pressure.
Fahrenheit (°F): This scale is predominantly used in the United States. It defines the freezing point of water at 32°F and the boiling point at 212°F at standard atmospheric pressure.
The difference in the scales lies in the size of their degrees and the zero points. A Celsius degree represents a larger temperature change than a Fahrenheit degree. This is why a seemingly small change in Celsius can translate to a significant change in Fahrenheit, and vice versa.
Converting 400°F to Celsius: The Formula
The formula for converting Fahrenheit to Celsius is:
°C = (°F - 32) × 5/9
Let's apply this to our 400°F:
°C = (400 - 32) × 5/9 = 368 × 5/9 = 204.44°C (approximately)
Therefore, 400 degrees Fahrenheit is approximately equal to 204.44 degrees Celsius.
Practical Applications of 204.44°C (400°F)
This temperature, whether expressed in Fahrenheit or Celsius, signifies a high heat level with diverse applications across various fields:
1. Cooking and Baking:
- Roasting: Many recipes call for high-temperature roasting, particularly for meats and vegetables to achieve a crispy exterior and tender interior. 400°F (204.44°C) is a common roasting temperature for achieving this.
- Baking: Certain baked goods, like some breads and pastries, require high heat for initial oven spring and proper browning. However, precise temperatures often depend on the recipe and oven.
- Grilling: Direct grilling at this temperature works well for searing meats and giving them a smoky flavor.
2. Industrial Processes:
- Metalworking: Many metalworking processes, such as annealing, tempering, and forging, involve heating materials to specific temperatures. 400°F (204.44°C) might be used for certain types of heat treatment.
- Chemical Processes: Several industrial chemical reactions require high temperatures, and 400°F (204.44°C) could be a part of these procedures.
- Manufacturing: Various manufacturing processes use heating elements at this temperature range for shaping, curing, or other transformations of materials.
3. Scientific Experiments:
- Laboratory settings: Many scientific experiments involving heating require precise temperature control, and 404.44°C could be used in many chemical and physical experiments.
- Material science: Studying the properties of materials at high temperatures is common in materials science research, often involving furnaces capable of reaching 400°F (204.44°C) or higher.
4. Home Applications:
- Oven Cleaning: Self-cleaning ovens often operate at temperatures around 400°F (204.44°C) to burn away food residue. However, it's crucial to follow the manufacturer's instructions carefully.
Beyond the Conversion: Understanding Heat and Temperature
While the conversion itself is straightforward, it's essential to understand the broader implications of heat and temperature.
Heat is the transfer of thermal energy from a hotter object to a colder object. It's measured in units like joules or calories.
Temperature is a measure of the average kinetic energy of the particles within a substance. Higher temperatures indicate faster-moving particles.
The relationship between heat and temperature isn't always linear. Different materials have different specific heat capacities, meaning they require different amounts of heat to raise their temperature by the same amount. For instance, water has a high specific heat capacity, requiring more energy to heat up compared to, say, metal.
Safety Precautions When Working with High Temperatures
Working with temperatures around 400°F (204.44°C) necessitates caution:
- Burns: Direct contact with hot surfaces can cause severe burns. Always use appropriate safety gear, such as oven mitts, heat-resistant gloves, and protective clothing.
- Fire Hazards: High temperatures can ignite flammable materials. Ensure proper ventilation and keep flammable substances away from heat sources.
- Equipment Safety: Always follow the manufacturer's instructions when using ovens, furnaces, or other equipment capable of reaching high temperatures. Regularly inspect equipment for any signs of damage or malfunction.
Common Misconceptions about Temperature Conversions
- Linearity: The conversion between Celsius and Fahrenheit isn't linear. A 10°C increase doesn't equal a 10°F increase.
- Zero Point: The zero points on the two scales are different. 0°C doesn't mean there is no heat; it's the freezing point of water under standard atmospheric pressure.
Advanced Applications and Further Exploration
For more in-depth understanding, exploring thermodynamics and heat transfer principles will provide a comprehensive perspective on the behavior of materials at high temperatures. This includes understanding concepts like thermal expansion, heat conductivity, and convection.
Conclusion
Converting 400°F to Celsius (approximately 204.44°C) is a simple calculation with far-reaching implications across various disciplines. Understanding the temperature scales, their practical applications, and safety precautions associated with high temperatures is crucial for anyone working with heat in any context – from cooking enthusiasts to industrial engineers and scientists. This guide serves as a foundational understanding, encouraging further exploration into the fascinating world of thermodynamics and heat transfer. Remember to always prioritize safety when working with high temperatures.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Percent Of 10 Is 25
Apr 01, 2025
-
What Is The Reciprocal Of 2
Apr 01, 2025
-
How Many Cups In 48 Oz Of Water
Apr 01, 2025
-
Is Baking Soda An Element Or A Compound
Apr 01, 2025
-
33 Out Of 50 As A Percentage
Apr 01, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is 400 Degrees In Celsius . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
