What Is The Number Under The Element
Kalali
Apr 02, 2025 · 6 min read
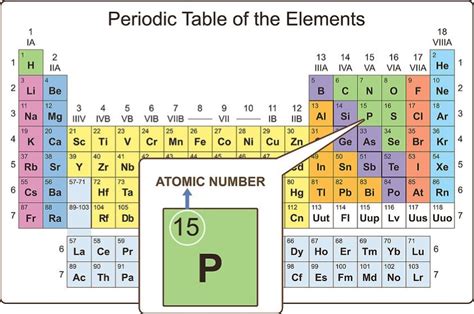
Table of Contents
What is the Number Under the Element? Decoding the Periodic Table
The periodic table, that iconic chart adorning countless science classrooms, is more than just a colorful arrangement of elements. It's a meticulously organized system revealing fundamental properties and relationships between the building blocks of matter. A crucial aspect of this organization lies in the numbers found beneath each element's symbol – atomic numbers. Understanding what these numbers represent is key to grasping the essence of chemistry and the behavior of matter.
Understanding Atomic Numbers: The Foundation of the Periodic Table
The number positioned beneath each element's symbol on the periodic table is its atomic number. This number represents the number of protons found in the nucleus of a single atom of that element. Protons, along with neutrons, constitute the atom's nucleus, while electrons orbit the nucleus in shells or energy levels.
Why are atomic numbers so important?
-
Unique Identification: Every element possesses a unique atomic number. This makes it the definitive identifier of an element. No two elements share the same atomic number. For instance, hydrogen's atomic number is 1, helium's is 2, and lithium's is 3, and so on. This unique identifier is fundamental to understanding the chemical properties of each element.
-
Defining Properties: The atomic number directly influences an element's chemical properties. The number of protons determines the number of electrons in a neutral atom, which, in turn, governs how the atom interacts with other atoms to form chemical bonds. This underlies the element's reactivity, its ability to form compounds, and its overall chemical behavior.
-
Organizing the Periodic Table: The periodic table is arranged in ascending order of atomic number. This arrangement is not arbitrary; it reflects the periodic recurrence of similar chemical properties in elements with increasing atomic numbers. Elements in the same group (vertical column) exhibit similar chemical behaviors due to similar electron configurations.
-
Isotopes and Atomic Mass: While the atomic number remains constant for a given element, the number of neutrons in the nucleus can vary. These variations create isotopes of the same element. Isotopes have the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons. The atomic mass listed on the periodic table is a weighted average of the masses of all naturally occurring isotopes of an element. The atomic number, however, remains consistent for all isotopes of an element.
Delving Deeper: Protons, Neutrons, and Electrons
To fully appreciate the significance of the atomic number, let's examine the subatomic particles that comprise an atom:
Protons: The Defining Particle
Protons are positively charged subatomic particles located within the atom's nucleus. Their number, as defined by the atomic number, dictates the element's identity and chemical properties. The positive charge of protons is crucial for the atom's overall neutrality, as it balances the negative charge of the electrons.
Neutrons: Nuclear Stability
Neutrons are electrically neutral particles found in the atom's nucleus. They contribute to the atom's mass but do not directly participate in chemical bonding. However, the number of neutrons significantly influences an atom's stability. Different isotopes of an element vary in the number of neutrons, leading to differences in stability – some isotopes are radioactive while others are stable.
Electrons: Chemical Behavior
Electrons are negatively charged subatomic particles that orbit the nucleus in specific energy levels or shells. The number of electrons in an atom, which is equal to the number of protons in a neutral atom, determines its chemical reactivity. Electrons participate in chemical bonds, forming connections between atoms to create molecules and compounds. The arrangement of electrons in energy levels dictates an element's position within the periodic table and governs its chemical behavior.
The Periodic Table's Structure and Atomic Numbers
The arrangement of the periodic table is directly linked to atomic numbers and electron configurations. Elements are organized in rows (periods) and columns (groups) based on their atomic numbers and recurring chemical properties.
Periods: Electron Shells
Each row or period on the periodic table represents an electron shell. Elements within the same period have the same number of electron shells. As you move across a period from left to right, the atomic number increases, and one electron is added to the outermost electron shell. This gradual filling of the outermost shell leads to changes in chemical properties across the period.
Groups: Electron Configurations and Chemical Properties
Each column or group on the periodic table contains elements with similar electron configurations in their outermost shells – also known as valence electrons. This similarity in valence electron configuration leads to similar chemical properties. Elements in the same group tend to react similarly with other elements and form similar types of compounds. For example, elements in Group 1 (alkali metals) are highly reactive, readily losing one electron to form a +1 ion.
Beyond the Basics: Applications of Atomic Numbers
The understanding of atomic numbers extends far beyond the fundamental concepts of chemistry. It has numerous applications in various scientific fields:
-
Nuclear Chemistry: Atomic numbers are crucial in nuclear reactions, where elements undergo transformations through changes in their nuclei. Understanding the atomic numbers of the elements involved is essential for predicting the products of nuclear reactions and analyzing nuclear processes.
-
Spectroscopy: Atomic numbers are related to the characteristic spectral lines of elements. When excited, atoms emit light at specific wavelengths that are unique to the element. Spectroscopy utilizes this principle to identify and quantify elements in various samples.
-
Material Science: The atomic number plays a role in determining the properties of materials. The arrangement and interaction of atoms, determined by their atomic numbers and electron configurations, affect the material's mechanical, electrical, and other properties.
-
Nuclear Medicine: Radioisotopes, isotopes with unstable nuclei, are widely used in medical imaging and therapy. Knowing the atomic number and the nature of the radioactive decay allows for targeted applications in medical diagnoses and treatment.
Conclusion: Atomic Numbers – The Key to Understanding Matter
The number under the element on the periodic table – the atomic number – is more than just a numerical value. It is the fundamental identifier of an element, dictating its chemical properties, its position on the periodic table, and its behavior in various chemical and physical processes. Understanding atomic numbers unlocks the secrets of matter, providing insights into the behavior of atoms, the formation of molecules, and the properties of materials. From the simplest chemical reactions to complex nuclear processes, atomic numbers serve as a cornerstone in our understanding of the world around us. Its importance extends across diverse scientific fields, demonstrating the profound significance of this seemingly simple number in unlocking the complexities of the universe. A deep understanding of atomic numbers is paramount for anyone exploring the fascinating world of chemistry and beyond.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Number Is 40 Percent Of 160
Apr 03, 2025
-
How Many Inches In 67 Cm
Apr 03, 2025
-
Which Are Two Ways A Population Can Decrease In Size
Apr 03, 2025
-
Which Products Are The Result Of A Neutralization Reaction
Apr 03, 2025
-
Which Planets Orbit Around The Sun Is Most Nearly Circular
Apr 03, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Number Under The Element . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
