What Is The Wavelength Of A 2.99 Hz Wave
Kalali
Apr 01, 2025 · 5 min read
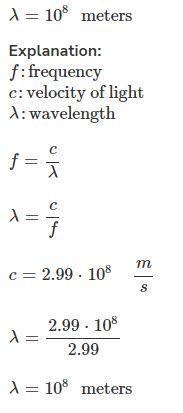
Table of Contents
What is the Wavelength of a 2.99 Hz Wave? Understanding Frequency and Wavelength
The question "What is the wavelength of a 2.99 Hz wave?" requires understanding the fundamental relationship between frequency and wavelength, particularly within the context of wave propagation. This relationship is crucial in various fields, from understanding radio waves and sound to analyzing seismic activity and even the behavior of light. Let's delve into the details.
Understanding Frequency and Wavelength
Before we calculate the wavelength, let's clarify the key terms:
-
Frequency (f): This refers to the number of complete wave cycles that pass a given point per unit of time. It's typically measured in Hertz (Hz), where 1 Hz represents one cycle per second. In our case, we have a frequency of 2.99 Hz.
-
Wavelength (λ): This is the distance between two consecutive corresponding points on a wave, such as two adjacent crests or troughs. It's typically measured in meters (m), centimeters (cm), or other units of length.
-
Wave Speed (v): This represents how fast the wave travels through a medium. The speed is dependent on the properties of the medium (e.g., air, water, solid). It's measured in meters per second (m/s).
The Fundamental Relationship: The Wave Equation
The connection between frequency, wavelength, and wave speed is elegantly expressed by the wave equation:
v = fλ
Where:
- v is the wave speed (m/s)
- f is the frequency (Hz)
- λ is the wavelength (m)
This equation tells us that the speed of a wave is the product of its frequency and wavelength. If we know any two of these values, we can easily calculate the third.
Calculating the Wavelength of a 2.99 Hz Wave
To determine the wavelength of our 2.99 Hz wave, we need to know the wave speed (v). The problem is that the wave speed is highly dependent on the type of wave and the medium through which it travels. A 2.99 Hz wave could be:
- A sound wave: The speed of sound varies considerably depending on the medium (air, water, steel, etc.) and temperature. In dry air at 20°C, the speed of sound is approximately 343 m/s.
- An electromagnetic wave (radio wave, etc.): Electromagnetic waves travel at the speed of light in a vacuum, approximately 299,792,458 m/s (often approximated as 3 x 10<sup>8</sup> m/s). The speed will be slightly slower in other media.
- An ocean wave: The speed of an ocean wave is dependent on water depth, wavelength, and other factors, making it complex to determine without more information.
- A seismic wave: Seismic waves have varying speeds depending on the type of wave (P-wave, S-wave) and the properties of the Earth's materials.
Therefore, we cannot definitively calculate the wavelength without knowing the type of wave and the medium.
Examples: Calculating Wavelength in Different Scenarios
Let's illustrate with some examples:
1. Sound Wave in Air:
Assuming our 2.99 Hz wave is a sound wave traveling in dry air at 20°C (v ≈ 343 m/s), we can use the wave equation:
λ = v / f = 343 m/s / 2.99 Hz ≈ 114.7 m
This means the wavelength of the 2.99 Hz sound wave in air would be approximately 114.7 meters.
2. Electromagnetic Wave in Vacuum:
If our 2.99 Hz wave is an electromagnetic wave (like a radio wave) traveling in a vacuum (v ≈ 3 x 10<sup>8</sup> m/s):
λ = v / f = (3 x 10<sup>8</sup> m/s) / 2.99 Hz ≈ 1.003 x 10<sup>8</sup> m
This translates to a wavelength of approximately 100,300,000 meters, or 100,300 kilometers – an incredibly long wavelength! This is typical for very low-frequency radio waves.
3. The Importance of Specifying the Medium
These examples clearly demonstrate the critical importance of specifying the type of wave and the medium through which it travels. A 2.99 Hz wave in air will have a drastically different wavelength compared to the same frequency wave traveling through a vacuum.
Low-Frequency Waves and Their Applications
Waves with frequencies as low as 2.99 Hz are typically found in the extremely low-frequency (ELF) range of the electromagnetic spectrum. These waves have several interesting applications and characteristics:
-
Extremely Long Wavelengths: As demonstrated, ELF waves have extremely long wavelengths, allowing them to penetrate the Earth's surface and even seawater to a significant depth.
-
Communication: ELF waves are used for communication with submarines deep underwater, where higher-frequency radio waves are absorbed or reflected. The long wavelengths allow for efficient penetration of the conductive seawater.
-
Natural Phenomena: Natural phenomena such as lightning strikes can generate ELF waves. Studying these waves provides valuable insights into atmospheric electricity and geophysical processes.
-
Geophysical Research: Researchers use ELF waves to study the Earth's internal structure and to monitor seismic activity. The waves' ability to penetrate deep into the Earth makes them a useful tool for geological investigations.
Conclusion: The Crucial Role of Context
In summary, the wavelength of a 2.99 Hz wave cannot be definitively determined without knowing the type of wave and the medium through which it propagates. The wave equation (v = fλ) is fundamental, but its application requires specific knowledge of the wave speed. We've illustrated how this leads to drastically different wavelengths depending on the scenario (e.g., sound in air versus electromagnetic waves in a vacuum). Understanding this relationship is crucial in various fields involving wave phenomena, particularly in applications involving low-frequency waves like ELF radio waves. The long wavelengths of these low-frequency waves open up unique opportunities for communication and geophysical exploration. Remember always to consider the context when working with wave properties.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
20 Oz Equals How Many Cups
Apr 03, 2025
-
How Many Inches Is 42 Centimeters
Apr 03, 2025
-
What Does A Turtle Look Like Without The Shell
Apr 03, 2025
-
Cuanto Es 31 Grados Fahrenheit En Centigrados
Apr 03, 2025
-
Which Linear Equation Shows A Proportional Relationship
Apr 03, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Wavelength Of A 2.99 Hz Wave . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
