Which Equation Represents A Proportional Relationship
Kalali
Mar 19, 2025 · 6 min read
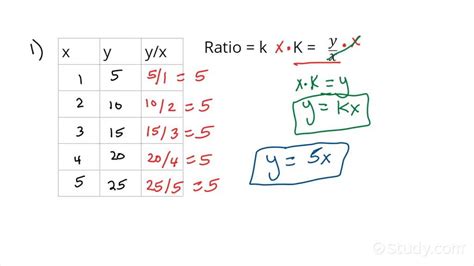
Table of Contents
Which Equation Represents a Proportional Relationship? A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding proportional relationships is crucial in various fields, from simple everyday calculations to complex scientific modeling. This comprehensive guide delves deep into identifying equations that represent proportional relationships, exploring different representations, and providing practical examples to solidify your understanding.
What is a Proportional Relationship?
A proportional relationship, also known as a direct proportion, exists between two variables when their ratio remains constant. This means that if one variable increases, the other increases proportionally, and if one decreases, the other decreases proportionally. The constant ratio is called the constant of proportionality, often represented by the letter k.
Key characteristics of a proportional relationship:
- Constant Ratio: The ratio between the two variables remains the same throughout the relationship.
- Origin Point: The graph of a proportional relationship always passes through the origin (0,0).
- Linear Relationship: Proportional relationships are always linear, meaning they can be represented by a straight line.
Identifying Equations that Represent Proportional Relationships
The most straightforward way to represent a proportional relationship is through an equation of the form:
y = kx
Where:
- y and x are the two variables.
- k is the constant of proportionality. It represents the rate at which y changes with respect to x.
This equation clearly shows the direct relationship: as x increases, y increases proportionally, and vice-versa. The constant k determines the steepness of the line representing the relationship on a graph. A larger k indicates a steeper line, meaning a faster rate of change.
Examples of Equations Representing Proportional Relationships:
- y = 3x: This equation represents a proportional relationship with a constant of proportionality of 3. For every increase of 1 in x, y increases by 3.
- d = 60t: This equation could represent the distance (d) traveled at a constant speed of 60 mph over time (t). The constant of proportionality is 60.
- C = πd: This equation relates the circumference (C) of a circle to its diameter (d), with π (pi) as the constant of proportionality.
Equations that DO NOT Represent Proportional Relationships:
It's equally important to identify equations that do not represent proportional relationships. These typically involve additional constants or terms that disrupt the constant ratio.
- y = kx + b (where b ≠ 0): This is the equation of a line, but it's not a proportional relationship unless b = 0. The constant 'b' represents the y-intercept, meaning the line does not pass through the origin.
- y = kx²: This equation represents a quadratic relationship, not a proportional one. The ratio y/x is not constant.
- y = k/x: This is an inverse relationship, where as x increases, y decreases. It's not a proportional relationship.
- y = k√x: This is a square root relationship, also not proportional.
Graphical Representation of Proportional Relationships
Proportional relationships are always represented by a straight line passing through the origin (0,0) on a coordinate plane. The slope of this line is equal to the constant of proportionality (k).
How to identify a proportional relationship graphically:
- Check the origin: Does the line pass through the point (0,0)? If not, it's not a proportional relationship.
- Check the linearity: Is the relationship represented by a straight line? If not, it's not a proportional relationship.
- Calculate the slope: Choose two points on the line and calculate the slope (rise/run). If the slope is constant between any two points, it indicates a proportional relationship. The slope is equal to the constant of proportionality (k).
Real-World Examples of Proportional Relationships
Proportional relationships are prevalent in many real-world scenarios:
- Speed and Distance: The distance traveled at a constant speed is directly proportional to the time spent traveling. (d = st, where s is the speed)
- Cost and Quantity: The total cost of buying multiple identical items is directly proportional to the number of items purchased. (Total cost = price per item * number of items)
- Work and Time: The amount of work done at a constant rate is directly proportional to the time spent working. (Work = rate * time)
- Scaling Recipes: When you double a recipe, you double all the ingredients. The amount of each ingredient is proportional to the number of servings.
- Currency Conversion: The amount of one currency you can exchange for another is directly proportional to the exchange rate.
Solving Problems Involving Proportional Relationships
Solving problems involving proportional relationships often involves using the equation y = kx and solving for either y, x, or k, depending on what information is given.
Example:
A car travels at a constant speed of 50 mph. How far will it travel in 3 hours?
- Known: k (speed) = 50 mph, x (time) = 3 hours.
- Unknown: y (distance)
- Equation: y = kx
- Solution: y = 50 mph * 3 hours = 150 miles
Tables and Proportional Relationships
Another way to represent and identify proportional relationships is through tables. A table displaying a proportional relationship will show a constant ratio between the two variables.
Example:
| Hours Worked (x) | Total Earnings (y) | Ratio (y/x) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | $15 | $15 |
| 2 | $30 | $15 |
| 3 | $45 | $15 |
| 4 | $60 | $15 |
In this table, the ratio of total earnings (y) to hours worked (x) is consistently $15. This confirms a proportional relationship with a constant of proportionality of $15 per hour.
Distinguishing Proportional Relationships from Other Relationships
It’s crucial to differentiate proportional relationships from other types of relationships:
- Inverse Relationships: In an inverse relationship, as one variable increases, the other decreases. The equation representing this is typically of the form y = k/x.
- Non-linear Relationships: These relationships are not represented by a straight line. Examples include quadratic (y = ax² + bx + c), exponential (y = abˣ), and logarithmic relationships.
Advanced Concepts and Applications
The understanding of proportional relationships forms the foundation for more complex mathematical concepts:
- Linear Equations: Proportional relationships are a specific type of linear equation.
- Slope and Intercept: The slope of a line representing a proportional relationship is equal to the constant of proportionality, and the y-intercept is always 0.
- Similar Triangles: The ratios of corresponding sides of similar triangles are proportional.
- Scale Drawings and Maps: Scale drawings and maps utilize proportional relationships to represent larger objects or areas at a smaller scale.
Conclusion
Understanding which equation represents a proportional relationship is essential for solving problems in various fields. By recognizing the constant ratio, the linear graph passing through the origin, and the fundamental equation y = kx, you can confidently identify and work with proportional relationships. Remember to always look for the consistent ratio between variables and ensure the relationship aligns with the characteristics described above. This comprehensive guide provides a solid foundation for mastering this important mathematical concept and applying it to real-world situations. Through consistent practice and application, you can confidently navigate the world of proportional relationships and leverage their power in your studies and daily life.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is 38 Out Of 40 As A Percentage
Mar 19, 2025
-
High Frequency Wave Vs Low Frequency Wave
Mar 19, 2025
-
Temperate Deciduous Forest Oak Tree Adaptations
Mar 19, 2025
-
What Animals Can See Human Bioluminescence
Mar 19, 2025
-
Is Sour Taste A Physical Property
Mar 19, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Equation Represents A Proportional Relationship . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
