5 To The Power Of 0
Kalali
Mar 18, 2025 · 5 min read
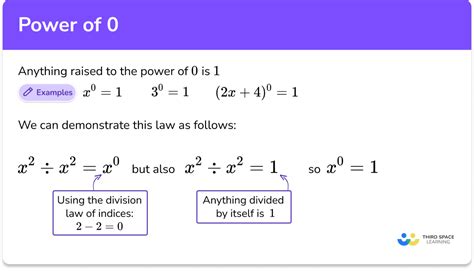
Table of Contents
5 to the Power of 0: Unraveling the Mystery of Exponents
The seemingly simple mathematical expression, 5⁰, often sparks curiosity and even confusion. Why does any number raised to the power of zero equal 1? This seemingly counterintuitive result is fundamental to understanding exponents and their broader applications in mathematics, science, and computer science. This article delves deep into the concept of 5⁰, exploring its derivation, its significance, and its implications within various mathematical contexts. We'll unravel the mystery surrounding this fundamental concept, making it clear and accessible to everyone, from beginners to those seeking a deeper understanding.
Understanding Exponents: A Foundation
Before diving into 5⁰, let's establish a solid understanding of exponents. An exponent, also known as a power or index, indicates how many times a number (the base) is multiplied by itself. For instance:
- 5² = 5 × 5 = 25 (5 raised to the power of 2, or 5 squared)
- 5³ = 5 × 5 × 5 = 125 (5 raised to the power of 3, or 5 cubed)
- 5⁴ = 5 × 5 × 5 × 5 = 625 (5 raised to the power of 4)
Notice a pattern? As the exponent increases by one, we multiply the previous result by the base (5). This pattern forms the bedrock of understanding how exponents work.
The Curious Case of 5⁰: Why Does it Equal 1?
Now, let's address the central question: why is 5⁰ = 1? There isn't a single, immediately obvious way to explain this, as multiplying 5 by itself zero times seems paradoxical. However, we can approach this from several perspectives:
1. The Pattern Approach: Maintaining Consistency
Let's extend the pattern we observed earlier:
- 5⁴ = 625
- 5³ = 125 (625 / 5)
- 5² = 25 (125 / 5)
- 5¹ = 5 (25 / 5)
Notice that as the exponent decreases by one, we divide the previous result by the base (5). Following this consistent pattern:
- 5⁰ = 5 / 5 = 1
This approach highlights the inherent consistency within the system of exponents. Maintaining this pattern logically leads to 5⁰ = 1.
2. The Identity Element of Multiplication
In mathematics, the identity element for multiplication is 1. This means that any number multiplied by 1 remains unchanged. Consider this:
- 5¹ = 5
- 5² = 5 × 5 = 5¹ × 5
- 5³ = 5 × 5 × 5 = 5² × 5
Following this logic, we can say:
- 5¹ = 5⁰ × 5
If we want to maintain this consistent relationship, then 5⁰ must equal 1, because only 1 multiplied by 5 will result in 5. This reinforces the idea that 5⁰ = 1 maintains the crucial multiplicative identity.
3. The Empty Product
In mathematics, the product of no numbers, also known as the empty product, is defined as 1. This concept is crucial in various areas, especially in combinatorics and algebra. Raising a number to the power of zero can be interpreted as the empty product. We are not multiplying any 5s together, hence the result is the multiplicative identity, 1.
4. Algebraic Justification: Power Rules
The rule aᵐ × aⁿ = aᵐ⁺ⁿ (where 'a' is the base, and 'm' and 'n' are exponents) is a fundamental property of exponents. Let's apply this:
- Consider 5¹ × 5⁰ = 5¹⁺⁰ = 5¹ = 5.
- If 5¹ × 5⁰ = 5, then it logically follows that 5⁰ must equal 1.
This approach demonstrates the consistency of exponent rules, reinforcing the conclusion that 5⁰ = 1.
Beyond 5⁰: The General Rule and its Applications
The principle extends beyond just 5. Any non-zero number raised to the power of zero equals 1. This is a fundamental rule in mathematics:
a⁰ = 1 (where 'a' is any non-zero number)
The case of 0⁰ is undefined, a topic for more advanced mathematical discussion that often involves limits and calculus.
The concept of raising a number to the power of zero has far-reaching implications:
- Polynomials: Understanding 5⁰ is critical in working with polynomials. For instance, the polynomial x² + 2x + 1 can be expressed as x² + 2x¹ + 1x⁰. This form is crucial for understanding and manipulating polynomial expressions.
- Combinatorics: The concept of an empty product, directly related to 5⁰ = 1, underpins many concepts in combinatorics, the study of arrangements and combinations.
- Calculus: The rule plays a crucial role in calculus, especially in dealing with derivatives and integrals involving exponential functions.
- Computer Science: In computer algorithms and data structures, the efficient handling of exponents and the understanding of 0⁰ (or its undefined nature) are essential aspects.
Addressing Common Misconceptions
Some common misunderstandings surrounding 5⁰ often arise:
- "Multiplying by zero": It's incorrect to interpret 5⁰ as multiplying 5 by zero. Exponents represent repeated multiplication of the base, not multiplication by the exponent itself.
- "The result should be zero": While it might seem intuitive that multiplying by nothing should result in zero, this is not how exponents are defined. The empty product defines the result as 1.
Conclusion: 5⁰ and the Power of Mathematical Consistency
The seemingly simple equation 5⁰ = 1 is more than just a mathematical fact; it's a manifestation of profound principles related to the consistent logic of the number system. Understanding this seemingly simple equation is fundamental to a deeper grasp of exponents, their applications in various mathematical branches, and ultimately, to a more profound appreciation of mathematical consistency and elegance. From polynomials and combinatorics to calculus and computer science, the concept of a number raised to the power of zero underpins many essential concepts. By thoroughly understanding this seemingly simple concept, we strengthen our foundational mathematical understanding and empower ourselves to tackle more complex mathematical challenges. The seemingly simple equation 5⁰ = 1 serves as a perfect example of how foundational mathematical principles can have significant implications in diverse fields. By understanding this and appreciating its deeper meaning, we pave the way for a stronger mathematical foundation and a broader perspective on mathematics as a cohesive and elegant system.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Do You Separate Sugar From Water
Mar 19, 2025
-
118 In Is How Many Feet
Mar 19, 2025
-
1 Meter 55 Cm To Feet
Mar 19, 2025
-
12 Oz Is Equal To How Many Ml
Mar 19, 2025
-
How To Find The Change In Enthalpy
Mar 19, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 5 To The Power Of 0 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
