How Do You Find The Circumference Of A Cylinder
Kalali
Mar 15, 2025 · 5 min read
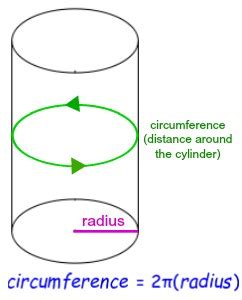
Table of Contents
How Do You Find the Circumference of a Cylinder? A Comprehensive Guide
Finding the circumference of a cylinder might seem straightforward, but understanding the nuances is crucial for accurate calculations in various fields, from engineering and manufacturing to architecture and design. This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of calculating the circumference of a cylinder, covering different approaches, practical examples, and troubleshooting common misconceptions. We'll explore the fundamental concepts, address potential pitfalls, and provide you with the tools to confidently tackle any cylinder circumference challenge.
Understanding the Cylinder's Anatomy
Before diving into the calculations, let's clarify what we're dealing with. A cylinder is a three-dimensional geometric shape with two parallel circular bases connected by a curved surface. Key components relevant to our circumference calculation include:
- Radius (r): The distance from the center of the circular base to any point on its edge.
- Diameter (d): Twice the radius (d = 2r). The distance across the circle through its center.
- Height (h): The perpendicular distance between the two circular bases. While crucial for calculating the cylinder's volume or surface area, the height is not directly involved in calculating the circumference.
Crucially, the circumference we are calculating refers to the circumference of the circular base of the cylinder. This is because the top and bottom bases are identical circles. Therefore, we will be using the formula for the circumference of a circle.
Calculating the Circumference: The Formula and its Application
The circumference (C) of a circle, and therefore the circumference of the circular base of a cylinder, is calculated using the following formula:
C = 2πr
Where:
- C represents the circumference.
- π (pi): A mathematical constant, approximately equal to 3.14159. For most practical purposes, using 3.14 is sufficient. However, using a calculator's built-in π function offers greater precision.
- r represents the radius of the circular base.
Alternatively, using the diameter:
C = πd
Step-by-Step Calculation Process
Let's break down the process with a clear example:
Problem: Find the circumference of a cylinder with a radius of 5 cm.
Step 1: Identify the Radius: The problem states the radius (r) is 5 cm.
Step 2: Choose the Formula: We'll use the formula C = 2πr.
Step 3: Substitute the Values: Substitute the value of the radius into the formula: C = 2 * π * 5 cm
Step 4: Calculate: Using π ≈ 3.14, the calculation is: C = 2 * 3.14 * 5 cm = 31.4 cm
Therefore, the circumference of the cylinder is approximately 31.4 cm.
Practical Applications and Real-World Examples
Understanding cylinder circumference calculations has far-reaching applications:
1. Engineering and Manufacturing:
- Designing pipes and tubes: Determining the circumference is essential for calculating the amount of material needed to manufacture pipes and tubes of specific diameters.
- Creating cylindrical containers: The circumference dictates the label size for packaging products in cylindrical containers.
- Machining and cutting: Accurate circumference calculations are crucial for machining processes that involve cylindrical components.
2. Architecture and Construction:
- Calculating the size of pillars and columns: Circular pillars and columns are common in architecture, and their circumference is crucial for determining material needs and structural integrity.
- Designing cylindrical tanks and silos: Circumference calculations are essential for determining the capacity and structural requirements of cylindrical tanks for liquids or granular materials.
- Estimating paint or coating requirements: Knowing the circumference helps estimate the amount of paint or coating needed for cylindrical structures.
3. Other Fields:
- Calculating the length of a circular track: Circumference is directly applicable to calculating the length of running tracks or racetracks.
- Determining the distance traveled by a rolling cylinder: One rotation of a cylinder corresponds to a distance equal to its circumference.
- Calculating the speed of rotating cylinders: The circumference is essential in calculating the linear speed of a point on the surface of a rotating cylinder.
Troubleshooting Common Mistakes and Misconceptions
Several common mistakes can lead to inaccurate circumference calculations. Let's address them:
- Confusing radius and diameter: A frequent error is using the diameter instead of the radius (or vice versa) in the formula. Remember that the diameter is twice the radius (d = 2r).
- Using an incorrect value for π: While 3.14 is a commonly used approximation, using a calculator's more precise value of π yields greater accuracy, especially for complex calculations.
- Incorrect unit conversion: Ensure consistent units throughout the calculation. If the radius is given in inches, the circumference will be in inches.
- Ignoring significant figures: Pay attention to the number of significant figures in the given data and round your final answer appropriately.
Advanced Concepts and Further Exploration
While the basic formula C = 2πr suffices for many applications, some situations require more sophisticated approaches:
- Cylinders with non-circular bases: While the term "cylinder" typically implies circular bases, some shapes resemble cylinders but have elliptical or other non-circular bases. Calculating the circumference in these cases requires using more complex formulas based on the specific geometry of the base.
- Calculating the curved surface area: While not directly related to circumference, understanding the curved surface area of a cylinder involves using the circumference (C) and height (h): Curved Surface Area = Ch.
- Working with different units: Be proficient in converting units (e.g., inches to centimeters, meters to feet) to maintain consistency in calculations.
Conclusion: Mastering Cylinder Circumference Calculations
Calculating the circumference of a cylinder is a fundamental skill with practical applications across numerous disciplines. By understanding the formula, following the step-by-step process, and avoiding common pitfalls, you can confidently tackle these calculations and apply your knowledge to real-world problems. Remember to choose the appropriate formula (based on radius or diameter), use an accurate value for π, and ensure consistent units throughout your calculations. With practice, you'll master this essential geometric concept and apply it effectively in diverse contexts. From designing mechanical parts to planning architectural structures, the ability to accurately calculate cylinder circumference is a valuable asset.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Do You Convert Moles To Liters
Mar 15, 2025
-
When The Speed Of An Object Is Doubled Its Momentum
Mar 15, 2025
-
Which Is Classified As An Inner Transition Element
Mar 15, 2025
-
Which Joint The Hip Or The Knee Is More Stable
Mar 15, 2025
-
How Many Light Years Is Sun From Earth
Mar 15, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Do You Find The Circumference Of A Cylinder . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
