How Many Light Years Is Sun From Earth
Kalali
Mar 15, 2025 · 5 min read
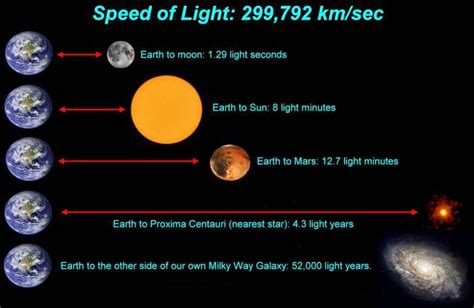
Table of Contents
How Many Light Years is the Sun From Earth? A Deep Dive into Stellar Distances
The question, "How many light years is the sun from Earth?" might seem deceptively simple. After all, we know the Sun is our star, the source of light and warmth that sustains life on our planet. But understanding the true distance, and the concept of a light-year itself, unveils a fascinating journey into the vastness of space and the intricacies of astronomical measurement. The short answer is incredibly simple: the Sun is not light-years away from Earth; it's much closer. But let's delve into why this is the case, and explore the related concepts that make understanding this distance so vital.
Understanding Light Years: A Unit of Astronomical Distance
Before we answer the primary question, let's clarify what a light-year actually represents. A light-year isn't a measure of time, as its name might suggest. Instead, it's a measure of distance. It represents the distance light travels in one year.
Given that the speed of light is approximately 299,792,458 meters per second (or roughly 186,282 miles per second), a light-year is an incredibly vast distance. To put it into perspective:
- One light-year is approximately 9.461 × 10<sup>15</sup> meters.
- One light-year is approximately 5.879 × 10<sup>12</sup> miles.
These numbers are so large that they're difficult to comprehend. It takes immense distances to even begin to approach the scale where light-years become a practical unit of measurement.
The Sun's Distance: An Astronomical Unit (AU)
The Sun's distance from the Earth is not measured in light-years. That's because it's relatively close to us in cosmic terms. Instead, astronomers use the Astronomical Unit (AU). One AU is defined as the average distance between the Earth and the Sun.
One AU is approximately 149.6 million kilometers (or about 93 million miles). This distance is still enormous, but it's significantly smaller than the vast distances measured in light-years.
It's crucial to understand that the Earth's orbit around the Sun is elliptical, not perfectly circular. This means the distance between the Earth and the Sun varies throughout the year. The difference, however, is relatively small compared to the average distance.
Why Light-Years Aren't Used for the Sun-Earth Distance
Using light-years to measure the Sun's distance from Earth would be akin to measuring the length of your driveway in kilometers. While technically correct, it's unnecessarily cumbersome and doesn't provide a practical or easily understandable measurement. The AU is a much more suitable and intuitive unit for this relatively short (in cosmic terms) distance.
Calculating the Time it Takes for Sunlight to Reach Earth
Although the Sun isn't light-years away, the speed of light and the distance still have a significant impact on our daily lives. It takes approximately 8 minutes and 20 seconds for sunlight to travel from the Sun to the Earth. This means that what we see of the Sun is actually how it appeared 8 minutes and 20 seconds ago. Any changes on the Sun's surface wouldn't be visible to us on Earth until that time has passed.
The Significance of the Sun's Proximity
The Sun's relatively close proximity to Earth is critical for life as we know it. The consistent influx of solar energy provides the warmth and light necessary to sustain ecosystems, drive weather patterns, and enable photosynthesis in plants. Without the Sun at this distance, Earth would be a vastly different, and likely uninhabitable, planet.
Exploring Other Celestial Distances: Where Light-Years Become Relevant
While light-years aren't necessary for understanding the Sun-Earth distance, they become essential when dealing with more distant celestial objects. Consider these examples:
-
Proxima Centauri: The closest star to our solar system, Proxima Centauri, is approximately 4.24 light-years away. This means the light we see from it today left the star over four years ago.
-
Sirius: One of the brightest stars in the night sky, Sirius is approximately 8.6 light-years away.
-
Andromeda Galaxy: The closest major galaxy to our own Milky Way galaxy, Andromeda, is approximately 2.537 million light-years away. The light we see from Andromeda today started its journey millions of years ago, offering us a glimpse into the galaxy's distant past.
These distances highlight the immense scale of the universe and the significance of light-years as a unit of measurement for comprehending such vastness.
Methods for Measuring Astronomical Distances
Astronomers employ various sophisticated techniques to measure astronomical distances, depending on the scale involved. For relatively nearby objects like the Sun, radar ranging and triangulation are used. For more distant objects, methods like stellar parallax, spectroscopic parallax, and standard candles (like Cepheid variables and Type Ia supernovae) are employed. These methods rely on the principles of geometry, physics, and the known properties of celestial objects to determine distances accurately.
The Importance of Accurate Distance Measurement
Precise measurement of astronomical distances is crucial for numerous reasons. It helps us understand:
-
The structure and scale of the universe: Mapping the distances between celestial objects gives us a clearer picture of the universe's vastness and its organization.
-
The evolution of stars and galaxies: By understanding distances, we can study the lifecycle of stars and the formation of galaxies more accurately.
-
The expansion of the universe: Measuring distances to distant galaxies helps us understand the rate at which the universe is expanding.
-
The search for extraterrestrial life: Knowing distances to other stars and planetary systems allows us to prioritize targets in the search for habitable planets and extraterrestrial life.
Conclusion: A Cosmic Perspective
The question of how many light-years the Sun is from Earth reveals a crucial distinction between the relatively short distances within our solar system and the vast cosmic distances beyond. While the Sun is a mere 1 AU away, the concept of light-years allows us to grasp the immense scale of the universe and the incredible journeys undertaken by light from distant stars and galaxies. Understanding both the AU and the light-year, and the sophisticated methods used to measure these astronomical distances, provides a valuable window into the scale and complexity of the cosmos. The Sun's proximity allows life on Earth to flourish, but the vast distances of the universe inspire a sense of wonder and the ongoing quest for deeper understanding.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Is Orange Juice With Pulp A Homogeneous Mixture
Mar 15, 2025
-
Angle Properties Of A Circle Outside The Circle
Mar 15, 2025
-
Which Graph Represents The Rational Function
Mar 15, 2025
-
Which Applies To The Collision Theory
Mar 15, 2025
-
Which Would Allow Humans To Access Groundwater
Mar 15, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Many Light Years Is Sun From Earth . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
