How Many Lines Of Symmetry Does A Hexagon Has
Kalali
Mar 11, 2025 · 6 min read
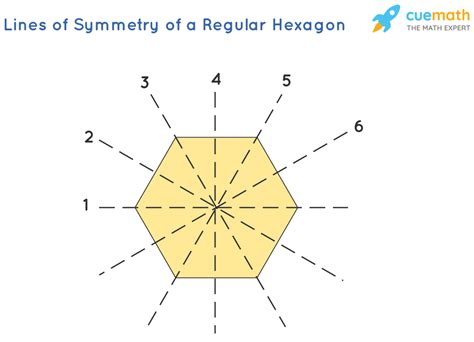
Table of Contents
How Many Lines of Symmetry Does a Hexagon Have? A Deep Dive into Geometry
Symmetry, a fundamental concept in mathematics and art, describes the harmonious arrangement of parts around a central axis or point. Understanding symmetry, particularly lines of symmetry, is crucial in various fields, from designing aesthetically pleasing objects to analyzing complex geometric shapes. This article delves into the fascinating world of symmetry, focusing specifically on the question: how many lines of symmetry does a hexagon have? We'll explore different types of hexagons, methods for identifying lines of symmetry, and the broader mathematical principles involved.
What is a Line of Symmetry?
Before we tackle hexagons, let's define our key term. A line of symmetry, also known as a line of reflection, is a line that divides a shape into two identical halves that are mirror images of each other. If you were to fold the shape along the line of symmetry, the two halves would perfectly overlap. This means every point on one side of the line has a corresponding point on the other side at an equal distance from the line.
Types of Hexagons
Hexagons are six-sided polygons. However, not all hexagons are created equal. The number of lines of symmetry a hexagon possesses depends heavily on its type. We'll focus on two primary categories:
1. Regular Hexagon
A regular hexagon is a hexagon where all six sides are equal in length, and all six interior angles are equal (each measuring 120 degrees). This high degree of regularity leads to a significant number of lines of symmetry.
2. Irregular Hexagon
An irregular hexagon is any hexagon that doesn't meet the criteria of a regular hexagon. Its sides and angles can vary in length and measure, resulting in fewer or no lines of symmetry. The number of lines of symmetry in an irregular hexagon can range from zero to three, depending on the specific arrangement of its sides and angles.
Finding Lines of Symmetry in a Regular Hexagon
Let's explore how to identify the lines of symmetry in a regular hexagon. Imagine a regular hexagon drawn on a piece of paper. We can systematically find the lines of symmetry by considering different types of lines that can pass through the hexagon:
1. Lines Connecting Opposite Vertices
A regular hexagon has three pairs of opposite vertices. A line drawn connecting any pair of opposite vertices will be a line of symmetry. Folding the hexagon along any of these lines will result in perfect overlap of the two halves. This gives us three lines of symmetry.
2. Lines Bisecting Opposite Sides
Similarly, a regular hexagon has three pairs of opposite sides. A line drawn perpendicularly bisecting any pair of opposite sides will also be a line of symmetry. This again divides the hexagon into two identical mirror halves, providing us with another three lines of symmetry.
Total Lines of Symmetry in a Regular Hexagon
Combining the lines of symmetry connecting opposite vertices and those bisecting opposite sides, we find that a regular hexagon possesses a total of six lines of symmetry. These six lines intersect at the center of the hexagon, creating a visually stunning and mathematically significant pattern.
Lines of Symmetry in Irregular Hexagons: A Case-by-Case Analysis
Unlike regular hexagons, irregular hexagons exhibit far less predictable symmetry. The number of lines of symmetry can range from zero to a maximum of three, depending on the specific configuration of the hexagon's sides and angles. Determining the lines of symmetry for an irregular hexagon often requires careful visual inspection and sometimes the application of geometric principles.
Here's a breakdown of possibilities:
-
Zero Lines of Symmetry: Most irregular hexagons will have no lines of symmetry. This occurs when there's no consistent pattern or mirror image relationship between the sides and angles.
-
One Line of Symmetry: It's possible for an irregular hexagon to possess one line of symmetry. This line would divide the hexagon into two mirror-image halves, but the rest of the shape would lack any further symmetry.
-
Two Lines of Symmetry: An irregular hexagon could have two lines of symmetry, possibly intersecting at a point within the hexagon or at one of the vertices.
-
Three Lines of Symmetry: This is the maximum number of lines of symmetry an irregular hexagon can have. These lines would likely intersect at a point within the hexagon, creating a pattern with three-fold rotational symmetry. Such hexagons display a degree of internal order, even if they're not perfectly regular.
Symmetry and Rotational Symmetry
It's important to distinguish between lines of symmetry and rotational symmetry. While a regular hexagon has six lines of symmetry, it also possesses rotational symmetry of order six. This means that it can be rotated about its center by multiples of 60 degrees and still appear unchanged. Many shapes possess both types of symmetry, but the presence of one doesn't automatically imply the other. An irregular hexagon might have rotational symmetry without having any lines of symmetry.
Applications of Hexagonal Symmetry
The unique symmetry properties of hexagons, particularly regular hexagons, make them incredibly useful in various fields:
-
Nature: Honeycomb structures in beehives are a prime example of hexagonal symmetry in nature. The hexagonal cells maximize space efficiency and structural strength. Similar hexagonal patterns are also found in certain crystals and other natural formations.
-
Engineering and Design: Hexagonal shapes are used extensively in engineering and design due to their strength and stability. Hexagonal bolts, nuts, and tiles are common examples. The symmetric distribution of forces in a hexagon makes it well-suited for load-bearing applications.
-
Art and Architecture: Hexagonal patterns have inspired artists and architects for centuries. The visually appealing nature of hexagonal symmetry leads to aesthetically pleasing designs in various forms of art and architecture.
-
Mathematics and Geometry: Hexagons play a significant role in advanced mathematical concepts such as tessellations (covering a plane with shapes without gaps or overlaps). The regular hexagon is one of only three regular polygons that can tessellate the plane.
Conclusion: Understanding the Importance of Symmetry
The question of how many lines of symmetry a hexagon has underscores the importance of understanding symmetry in various aspects of life, from the natural world to engineering and design. While a regular hexagon boasts six lines of symmetry, the number for irregular hexagons is more variable. Understanding the distinctions between different types of hexagons and the methods for identifying lines of symmetry is crucial for appreciating the beauty and functionality of this versatile geometric shape. By analyzing symmetry, we unlock a deeper understanding of shape, pattern, and the underlying mathematical principles that govern our world. Further exploration into the rich field of geometry will reveal even more fascinating connections between symmetry, patterns, and practical applications.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Inches In 32 Feet
Mar 11, 2025
-
What Is The Percent Of 1 12
Mar 11, 2025
-
How Many Valence Electrons Are In Calcium
Mar 11, 2025
-
Explain How The Biosphere Interacts With The Atmosphere
Mar 11, 2025
-
How To Find Speed Of A Wave
Mar 11, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Many Lines Of Symmetry Does A Hexagon Has . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
