How Many Neutrons Does Potassium Have
Kalali
Mar 10, 2025 · 5 min read
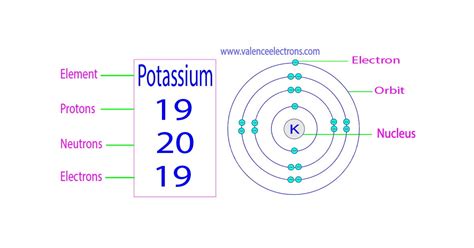
Table of Contents
How Many Neutrons Does Potassium Have? Exploring Isotopes and Atomic Structure
Potassium, a vital element for human health and a key player in various biological processes, presents an intriguing challenge when it comes to determining the exact number of neutrons it possesses. The answer isn't a simple single number, but rather a range depending on the specific isotope of potassium being considered. This article will delve deep into the world of isotopes, atomic structure, and the nuances of potassium's neutron count, providing a comprehensive understanding for students, researchers, and anyone curious about the fascinating world of atomic physics.
Understanding Atomic Structure: Protons, Neutrons, and Electrons
Before we tackle the specifics of potassium's neutron count, let's establish a firm grasp of basic atomic structure. Every atom consists of three fundamental subatomic particles:
- Protons: Positively charged particles located in the atom's nucleus. The number of protons defines the element; all potassium atoms have 19 protons.
- Neutrons: Neutral particles (no charge) also residing in the nucleus. The number of neutrons can vary within the same element, leading to isotopes.
- Electrons: Negatively charged particles orbiting the nucleus in electron shells. The number of electrons typically equals the number of protons in a neutral atom.
The atomic number of an element represents the number of protons in its nucleus. Potassium's atomic number is 19, meaning every potassium atom possesses 19 protons. The mass number, on the other hand, is the sum of protons and neutrons in the nucleus. Since the number of neutrons can vary, the mass number isn't fixed for a given element.
Isotopes: The Key to Variable Neutron Counts
Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have the same number of protons but differ in the number of neutrons. This difference in neutron number leads to variations in the atom's mass. Different isotopes of the same element exhibit similar chemical properties but can have significantly different physical properties, particularly relating to radioactivity.
Potassium has three naturally occurring isotopes:
- Potassium-39 (³⁹K): This is the most abundant isotope, making up approximately 93.3% of naturally occurring potassium. It has 19 protons and 20 neutrons (19 + 20 = 39).
- Potassium-40 (⁴⁰K): A radioactive isotope, ⁴⁰K constitutes about 0.012% of natural potassium. It possesses 19 protons and 21 neutrons (19 + 21 = 40). This isotope is notable for its role in potassium-argon dating, a method used in geology to determine the age of rocks. The radioactive decay of ⁴⁰K to ⁴⁰Ar is the basis of this technique.
- Potassium-41 (⁴¹K): The third naturally occurring isotope, ⁴¹K makes up roughly 6.7% of natural potassium. It contains 19 protons and 22 neutrons (19 + 22 = 41).
Calculating Neutron Count: A Simple Formula
Determining the number of neutrons in a potassium atom is straightforward once you know the isotope. The formula is:
Number of Neutrons = Mass Number - Atomic Number
For example:
- ³⁹K: 39 - 19 = 20 neutrons
- ⁴⁰K: 40 - 19 = 21 neutrons
- ⁴¹K: 41 - 19 = 22 neutrons
This simple calculation highlights the variable nature of the neutron count in potassium atoms.
The Significance of Potassium Isotopes in Various Fields
The different isotopes of potassium play significant roles in various scientific disciplines:
1. Biology and Medicine: Potassium is crucial for various biological processes, including nerve impulse transmission, muscle contraction, and maintaining fluid balance. The radioactive isotope ⁴⁰K, although present in small amounts, contributes to the overall radiation exposure experienced by living organisms. Its decay is also utilized in medical imaging techniques.
2. Geology and Geochronology: The radioactive decay of ⁴⁰K to ⁴⁰Ar forms the basis of potassium-argon dating, a powerful tool used to date rocks and minerals. This technique is crucial in understanding geological timescales and the Earth's history.
3. Nuclear Physics and Research: Studies involving potassium isotopes contribute to a better understanding of nuclear reactions, radioactive decay processes, and the properties of atomic nuclei. The radioactive isotope ⁴⁰K is often used as a tracer in various research applications.
4. Environmental Science: The isotopic composition of potassium in different environmental samples (water, soil, plants) can provide valuable insights into environmental processes, including nutrient cycling, water movement, and pollution sources.
Beyond Natural Isotopes: Artificial Potassium Isotopes
While the three isotopes mentioned above are naturally occurring, scientists can create artificial potassium isotopes through nuclear reactions in laboratories. These artificial isotopes often have shorter half-lives and are used for specialized research purposes. These isotopes typically have either more or fewer neutrons than the natural isotopes. Their properties are heavily studied to broaden our understanding of nuclear physics and potentially for various applications in medicine and other fields.
Conclusion: A Deeper Dive into Atomic Diversity
The question "How many neutrons does potassium have?" doesn't have a single answer. The number of neutrons varies depending on the specific potassium isotope. Understanding this variation is fundamental to grasping the complexities of atomic structure, isotopic diversity, and the crucial roles different potassium isotopes play in various scientific fields, from biology and medicine to geology and nuclear physics. This exploration of potassium isotopes serves as a microcosm of the vast and fascinating world of atomic physics and its implications across numerous scientific disciplines. Further research into the specific properties and applications of each potassium isotope will continue to expand our knowledge and potential applications of this essential element. The study of isotopes, therefore, is not merely an academic pursuit but a cornerstone of advancement in numerous scientific and technological fields.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
43 Out Of 50 Is What Percent
Mar 11, 2025
-
How Many Sides Does An Octagon Has
Mar 11, 2025
-
Why The Noble Gases Are Unreactive
Mar 11, 2025
-
How Many Lines Of Symmetry Does A Hexagon Has
Mar 11, 2025
-
How Much Is 157 Cm In Feet
Mar 11, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Many Neutrons Does Potassium Have . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
