How Will Cellular Respiration Affect Oxygen Levels
Kalali
Mar 19, 2025 · 6 min read
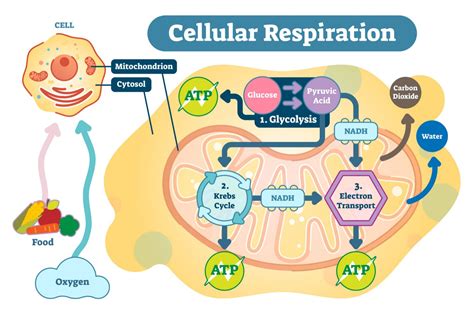
Table of Contents
How Cellular Respiration Affects Oxygen Levels: A Deep Dive
Cellular respiration, the process by which cells break down glucose to produce energy, plays a crucial role in regulating oxygen levels in various environments. Understanding this intricate relationship is fundamental to grasping ecological balances, physiological functions, and even certain industrial processes. This comprehensive article explores the multifaceted impact of cellular respiration on oxygen levels, delving into the mechanisms, consequences, and broader implications.
The Core Mechanism: Oxygen as the Final Electron Acceptor
At the heart of cellular respiration lies the electron transport chain (ETC), located within the inner mitochondrial membrane. This chain of protein complexes acts as a conduit for electrons harvested from the breakdown of glucose during glycolysis and the citric acid cycle (Krebs cycle). Crucially, oxygen serves as the terminal electron acceptor in this chain. Without oxygen, the ETC grinds to a halt, drastically affecting energy production.
What happens when oxygen is absent?
In the absence of oxygen, anaerobic respiration takes over. This process is far less efficient than aerobic respiration (which utilizes oxygen), yielding significantly less ATP (adenosine triphosphate), the cell's primary energy currency. Anaerobic respiration relies on alternative electron acceptors, such as sulfate or nitrate, producing byproducts like ethanol or lactic acid. These byproducts can have significant implications for the surrounding environment, as discussed later.
The Oxygen Consumption Rate: A Key Indicator
The rate of oxygen consumption during cellular respiration is a direct reflection of the metabolic activity of cells and tissues. Factors influencing this rate include:
- Temperature: Higher temperatures generally increase the rate of enzymatic reactions involved in cellular respiration, leading to higher oxygen consumption.
- Substrate Availability: The availability of glucose and other energy-yielding substrates directly influences the rate of respiration and consequently, oxygen demand.
- Hormonal Regulation: Hormones like adrenaline can significantly stimulate cellular respiration, increasing oxygen consumption.
- Activity Level: In multicellular organisms, physical activity drastically increases oxygen consumption as muscles demand more energy.
Cellular Respiration's Impact on Oxygen Levels in Different Contexts
The impact of cellular respiration on oxygen levels manifests differently across various scales, from the microscopic level within cells to the macroscopic level within ecosystems.
1. At the Cellular Level: Maintaining Oxygen Homeostasis
Within individual cells, the balance between oxygen consumption and supply is vital for survival. Cells maintain a delicate equilibrium by adjusting their respiration rates based on the availability of oxygen. When oxygen levels drop (hypoxia), cells switch to anaerobic respiration, albeit temporarily and inefficiently. Prolonged hypoxia can lead to cell damage or death.
2. In Tissues and Organs: Oxygen Delivery and Utilization
In multicellular organisms, the efficient delivery of oxygen to tissues and organs is critical. The circulatory system plays a crucial role in transporting oxygen from the lungs (or gills) to cells throughout the body. The rate of oxygen consumption by tissues dictates the demand placed on the circulatory system. Inadequate oxygen delivery leads to tissue hypoxia, potentially resulting in organ dysfunction or failure. This is particularly relevant in conditions like heart failure or respiratory diseases.
3. Within Ecosystems: Shaping Atmospheric Oxygen Levels
On a larger scale, the collective respiration of all living organisms significantly influences global oxygen levels. Photosynthesis, the process by which plants and other photosynthetic organisms produce oxygen, counterbalances the oxygen consumed during respiration. The balance between these two processes dictates the atmospheric oxygen concentration. Large-scale disturbances, such as deforestation or algal blooms, can disrupt this balance and affect oxygen levels.
The impact of deforestation: The removal of trees reduces the photosynthetic capacity of an ecosystem, leading to a decrease in oxygen production. This, coupled with the continued respiration of other organisms, can result in a local or even regional decline in oxygen levels.
Algal blooms and oxygen depletion (eutrophication): Excessive nutrient runoff into water bodies fuels rapid algal growth. When these algae die and decompose, bacteria consume large quantities of oxygen during their respiration, leading to hypoxia or anoxia (complete absence of oxygen) in the water, creating "dead zones" where aquatic life cannot survive.
4. In Industrial Settings: Bioreactors and Fermentation
Industrial processes, such as bioreactors used in the production of pharmaceuticals and biofuels, carefully manipulate oxygen levels to optimize cellular respiration. The design and operation of these bioreactors require a precise understanding of the interplay between oxygen supply and microbial respiration rates. Fermentation, an anaerobic process, is also used in various industries, including the production of alcoholic beverages and certain foods, where the absence of oxygen is crucial for the desired metabolic pathways.
Consequences of Altered Oxygen Levels Due to Cellular Respiration
Changes in oxygen levels, driven by shifts in cellular respiration, can have cascading effects across various biological systems.
1. Hypoxia and its Physiological Effects
Hypoxia, a condition of low oxygen levels, triggers a range of physiological responses, including increased heart rate, increased ventilation rate, and changes in blood flow distribution. Prolonged hypoxia can lead to cell damage, organ dysfunction, and ultimately, death. Examples include high-altitude sickness, where reduced atmospheric pressure leads to low blood oxygen levels, and various cardiovascular and respiratory diseases.
2. Anoxia and its devastating effects
Anoxia, the complete absence of oxygen, rapidly shuts down aerobic cellular respiration. This leads to rapid cell death in most organisms, particularly in oxygen-sensitive tissues like the brain and heart. Anoxic events can occur during heart attacks, strokes, or severe drowning incidents.
3. The Impacts of Excess Oxygen (Hyperoxia)
While less common than hypoxia, high oxygen levels (hyperoxia) can also be detrimental. Prolonged exposure to high partial pressures of oxygen can cause oxidative stress, damaging cellular components through the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS). This can contribute to lung damage (as seen in premature infants receiving supplemental oxygen) and other health problems.
Monitoring and Measuring Oxygen Levels Related to Cellular Respiration
Several methods are used to monitor and measure oxygen levels in various contexts:
- Oxygen sensors: These electrochemical sensors are widely used to measure dissolved oxygen in water or gaseous oxygen in air.
- Blood oxygen monitors (pulse oximetry): These non-invasive devices measure blood oxygen saturation, providing a vital indicator of oxygen delivery to tissues.
- Metabolic chambers: These specialized chambers are used to measure oxygen consumption rates in organisms, providing insights into their metabolic activity.
Conclusion: A Complex Interplay
Cellular respiration's impact on oxygen levels is a complex interplay of factors operating at various scales. Understanding this relationship is essential for advancing our knowledge in diverse fields, including medicine, ecology, and environmental science. Future research focusing on optimizing oxygen utilization in cellular respiration and understanding the impacts of climate change on global oxygen levels is crucial. By continually refining our knowledge of this fundamental process, we can better address challenges associated with oxygen availability and its crucial role in supporting life on Earth.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
33 Of 40 Is What Percent
Mar 19, 2025
-
How Did He Know That The Nucleus Was Positively Charged
Mar 19, 2025
-
The Carbon Atoms In Saturated Hydrocarbons
Mar 19, 2025
-
How Many Ml In 1 4 Oz
Mar 19, 2025
-
7 Out Of 24 As A Percentage
Mar 19, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Will Cellular Respiration Affect Oxygen Levels . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
