Is H20 On The Periodic Table
Kalali
Mar 29, 2025 · 5 min read
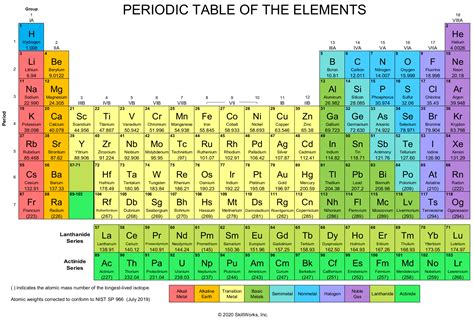
Table of Contents
Is H₂O on the Periodic Table? Understanding the Difference Between Elements and Compounds
The question, "Is H₂O on the periodic table?" is a common one, and the answer requires understanding the fundamental difference between elements and compounds. The short answer is no, H₂O (water) itself is not found on the periodic table. However, the elements that compose water, hydrogen (H) and oxygen (O), are prominently featured. This article delves deeper into the distinction, exploring the periodic table's structure, the nature of elements and compounds, and the specific properties of hydrogen and oxygen that allow them to form water.
The Periodic Table: A Catalog of Elements
The periodic table is a cornerstone of chemistry, organizing all known chemical elements in a structured grid. Each element occupies a unique square, containing its atomic number, symbol, and often, its atomic mass. These elements are the fundamental building blocks of all matter, indivisible by chemical means. They are defined by their atomic number, which represents the number of protons in their nucleus.
Key Features of the Periodic Table
- Atomic Number: The unique identifier of each element, representing the number of protons in its nucleus.
- Element Symbol: A shorthand abbreviation for the element's name (e.g., H for hydrogen, O for oxygen).
- Atomic Mass: The average mass of an atom of the element, considering the different isotopes.
- Periods and Groups: Elements are arranged in rows (periods) and columns (groups) based on their electronic configurations and recurring chemical properties. Groups represent elements with similar chemical behavior.
The periodic table showcases the fundamental building blocks of nature. It's not a list of every possible substance, but rather a catalog of the unique elements from which all substances, including compounds like H₂O, are constructed.
The Difference Between Elements and Compounds
The distinction between elements and compounds is crucial to understanding why H₂O isn't on the periodic table.
-
Elements: Elements are pure substances consisting of only one type of atom. They cannot be broken down into simpler substances by chemical means. Examples include hydrogen (H), oxygen (O), iron (Fe), and gold (Au).
-
Compounds: Compounds are substances formed by the chemical combination of two or more different elements in fixed proportions. These elements are bonded together through chemical bonds, resulting in a substance with properties different from its constituent elements. Water (H₂O) is a classic example, formed by the bonding of two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom.
Hydrogen (H): The Lightest Element
Hydrogen, with the atomic number 1, occupies the top-left corner of the periodic table. It's the most abundant element in the universe and plays a crucial role in many chemical processes. Its single proton and single electron define its unique properties.
Key Properties of Hydrogen:
- Highly Reactive: Hydrogen readily forms chemical bonds with other elements, especially oxygen.
- Low Density: It's the lightest element, with a very low density compared to other elements.
- Flammable: Hydrogen gas is highly flammable, reacting explosively with oxygen in the presence of an ignition source.
- Versatile Uses: Hydrogen is used in various applications, including fuel cells, ammonia production, and metal refining.
Oxygen (O): Essential for Life
Oxygen, with the atomic number 8, is another vital element found on the periodic table. It's the third most abundant element in the universe and is essential for respiration in most living organisms. Its eight protons and eight electrons contribute to its characteristic reactivity.
Key Properties of Oxygen:
- Highly Reactive: Oxygen readily reacts with many elements, forming oxides.
- Supports Combustion: Oxygen is a crucial component in combustion reactions, enabling the burning of fuels.
- Essential for Life: Oxygen is vital for aerobic respiration, the process by which organisms convert energy from food.
- Abundant in the Atmosphere: Oxygen makes up a significant portion of Earth's atmosphere, approximately 21%.
The Formation of Water (H₂O)
Water, H₂O, is formed when two hydrogen atoms covalently bond with one oxygen atom. This covalent bond involves the sharing of electrons between the atoms, creating a stable molecule. The unique properties of water arise from this specific bonding arrangement and the polarity of the molecule.
The Covalent Bond in Water:
The oxygen atom, with its higher electronegativity, attracts the shared electrons more strongly than the hydrogen atoms. This creates a polar molecule, with a slightly negative charge on the oxygen atom and slightly positive charges on the hydrogen atoms. This polarity is crucial for water's unique properties.
Properties of Water (H₂O):
Water's unique properties, arising from its molecular structure, make it essential for life on Earth:
- High Specific Heat Capacity: Water can absorb a significant amount of heat without a large temperature change, making it an effective temperature regulator.
- High Heat of Vaporization: A considerable amount of heat is required to convert liquid water to vapor, contributing to evaporative cooling.
- Universal Solvent: Water's polarity allows it to dissolve many ionic and polar substances, making it an excellent solvent for biological processes.
- High Surface Tension: The strong intermolecular forces in water contribute to its high surface tension.
- Density Anomaly: Ice is less dense than liquid water, causing ice to float, which has crucial ecological consequences.
Why H₂O Isn't on the Periodic Table: Recap
In summary, H₂O is not on the periodic table because the periodic table organizes elements, not compounds. H₂O is a compound, a chemically bonded combination of two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom. Hydrogen (H) and oxygen (O) are listed individually on the periodic table, representing their unique atomic structures and properties. Understanding this fundamental distinction is crucial for comprehending the basic principles of chemistry. The periodic table serves as the foundation upon which the vast diversity of chemical substances, including compounds like water, is built. The properties of H₂O are a direct consequence of the individual properties of H and O, and the way they interact to form a unique and essential molecule. The unique properties of water, resulting from the specific bonding of hydrogen and oxygen atoms, are responsible for its crucial role in supporting life on Earth. It's the interplay of these elements, and their chemical interactions, that give rise to the amazing complexity and diversity of the chemical world.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is Diameter Of A Cylinder
Apr 01, 2025
-
Least Common Multiple Of 6 And 7
Apr 01, 2025
-
How Many Centimeters Are In 2 M
Apr 01, 2025
-
What Is Depression On A Topographic Map
Apr 01, 2025
-
12 Oz Equal How Many Cups
Apr 01, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Is H20 On The Periodic Table . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
