Is Sand And Water A Homogeneous Mixture
Kalali
Mar 17, 2025 · 5 min read
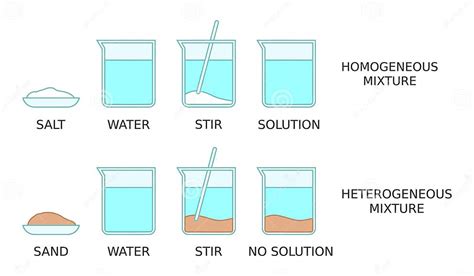
Table of Contents
Is Sand and Water a Homogeneous Mixture? A Deep Dive into Mixture Classification
The question of whether sand and water form a homogeneous mixture is a common one, particularly in introductory chemistry and science classes. The answer, however, isn't a simple yes or no. Understanding the nuances of mixture classification requires a closer look at the properties of both sand and water and the definition of homogeneity itself. This article will delve into the intricacies of this question, examining the characteristics of homogeneous and heterogeneous mixtures, exploring the behavior of sand and water, and finally arriving at a conclusive answer.
Understanding Homogeneous and Heterogeneous Mixtures
Before we can classify a sand and water mixture, we need to establish a firm understanding of the terms "homogeneous" and "heterogeneous." These terms describe the uniformity of a mixture at a macroscopic and microscopic level.
Homogeneous Mixtures: Uniformity at Every Level
A homogeneous mixture is one that has a uniform composition throughout. This means that no matter where you take a sample from the mixture, its properties—like density, color, and concentration of components—will be identical. At a microscopic level, the components are evenly distributed and intimately mixed. Examples include saltwater, air, and sugar dissolved in water. You cannot visually distinguish the individual components; they appear as a single phase.
Heterogeneous Mixtures: Visible Differences and Variations
In contrast, a heterogeneous mixture has a non-uniform composition. Different regions of the mixture will have varying properties. Visually, you can often distinguish the individual components. The components are not evenly dispersed, and distinct phases are observable. Examples include sand and pebbles in water, oil and water, and a salad.
Analyzing the Sand and Water Mixture
Now let's turn our attention to the specific case of sand and water. Sand is composed primarily of silicon dioxide (SiO2) particles, varying in size but generally ranging from microscopic to macroscopic. Water, of course, is H2O.
When sand is mixed with water, the sand particles do not dissolve. They remain as distinct solid particles suspended within the liquid water. This immediately suggests a heterogeneous mixture. Let's examine this further:
Visual Observation: The Defining Factor
The most straightforward way to determine if a mixture is homogeneous or heterogeneous is through visual observation. In a sand and water mixture, we can clearly see the sand particles suspended in the water. They are not uniformly distributed at the macroscopic level. This visual distinction immediately disqualifies it from being a homogeneous mixture.
Microscopic Examination: Further Confirmation
Even if we were to examine a small sample under a microscope, we would still observe the distinct sand particles separate from the water molecules. The components maintain their individual identities, and a uniform dispersion at a microscopic level is absent. This reinforces the classification of the mixture as heterogeneous.
Settling: A Telltale Sign of Heterogeneity
Over time, the sand particles in the water will settle due to gravity. This settling process is a characteristic feature of heterogeneous mixtures. In a homogeneous mixture, the components would remain evenly dispersed indefinitely. The sedimentation of sand clearly demonstrates the lack of uniform composition within the mixture.
Separation: Easy Division of Components
The ease with which we can separate the sand and water further underscores the heterogeneous nature of the mixture. Simple methods like decantation (carefully pouring off the water) or filtration (passing the mixture through a filter) can readily separate the two components. This is not possible with homogeneous mixtures where the components are intimately bound.
The Role of Particle Size and Dispersion
Some might argue that if we grind the sand into an extremely fine powder, it might appear more homogeneous. While the finer particles might initially remain suspended for a longer time, they will still eventually settle. The crucial factor isn't the size of the sand particles, but their ability to dissolve in water. Sand is insoluble, meaning its particles will always remain distinct from the water molecules, regardless of size. Even with extremely fine sand, the mixture would remain heterogeneous due to the lack of molecular-level interaction.
Furthermore, the concept of homogeneity refers to uniformity of composition, not just visual appearance. Even if we were to create a seemingly uniform slurry with extremely fine sand, if we were to take samples from different locations and analyze them (for example, through microscopic examination), the composition would not be perfectly uniform. There would be microscopic variations in the concentration of sand particles.
Beyond the Basics: Colloids and Suspensions
The sand and water mixture is a good example of a suspension. Suspensions are a type of heterogeneous mixture where solid particles are dispersed in a liquid. These particles are relatively large and will settle out over time. Another type of heterogeneous mixture is a colloid, where the dispersed particles are much smaller and don't settle as quickly. However, even colloids remain heterogeneous due to non-uniformity of composition at some level.
Conclusion: Sand and Water Remain Heterogeneous
Based on all the evidence presented, the definitive answer to the question is no, sand and water do not form a homogeneous mixture. The sand particles remain distinct from the water molecules, creating a heterogeneous mixture characterized by non-uniform composition, visual distinguishability of components, and the ability to easily separate the components. The size of the sand particles, while influencing the suspension time, does not change the fundamental nature of the mixture's heterogeneity. The visual observation, microscopic examination, settling behavior, and simple separation methods all undeniably point to a heterogeneous classification.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Sample Evidence Can Prove That A Null Hypothesis Is True
Mar 17, 2025
-
How Many Valence Electrons Does Calcium Ca Have
Mar 17, 2025
-
Common Multiples Of 4 5 6
Mar 17, 2025
-
How Do You Multiply Decimals Without A Calculator
Mar 17, 2025
-
In Eukaryotes Transcription Takes Place In The
Mar 17, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Is Sand And Water A Homogeneous Mixture . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
