What Is 35 In Roman Numerals
Kalali
Mar 24, 2025 · 5 min read
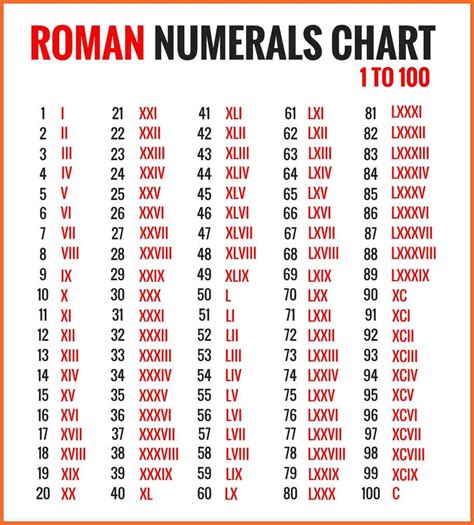
Table of Contents
What is 35 in Roman Numerals? A Deep Dive into Roman Numeral System
The question, "What is 35 in Roman numerals?" seems simple enough. A quick search will readily provide the answer: XXXV. However, understanding the why behind this representation unlocks a deeper appreciation of the Roman numeral system, its history, and its enduring relevance. This article will not only answer the initial question but will also delve into the intricacies of Roman numerals, exploring their origins, rules, and applications.
Understanding the Roman Numeral System
The Roman numeral system, unlike the decimal system we commonly use, is an additive and subtractive system. It utilizes seven basic symbols to represent numbers:
- I = 1
- V = 5
- X = 10
- L = 50
- C = 100
- D = 500
- M = 1000
These symbols are combined to represent larger numbers. The core principle is that smaller values preceding a larger value are subtracted, while smaller values following a larger value are added.
The Additive Principle
This principle is straightforward. To represent a number, simply add the values of the individual symbols. For example:
- XII = 10 + 1 + 1 = 12
- XXVII = 10 + 10 + 5 + 1 + 1 = 27
- LXIV = 50 + 10 + 5 - 1 = 64 (Note the subtractive principle coming into play)
The Subtractive Principle
The subtractive principle is what makes the Roman numeral system more efficient than simply stringing together symbols additively. This principle states that when a smaller value symbol precedes a larger value symbol, the smaller value is subtracted from the larger value. For instance:
- IV = 5 - 1 = 4 (Instead of writing IIII)
- IX = 10 - 1 = 9 (Instead of VIIII)
- XL = 50 - 10 = 40 (Instead of XXXX)
- XC = 100 - 10 = 90 (Instead of LXXXX)
- CD = 500 - 100 = 400 (Instead of CCCC)
- CM = 1000 - 100 = 900 (Instead of DCCCC)
This subtractive principle significantly reduces the number of symbols needed to represent certain numbers.
Deconstructing XXXV: 35 in Roman Numerals
Now, let's break down the representation of 35 in Roman numerals: XXXV.
Following the additive and subtractive principles:
- XXX represents 30 (10 + 10 + 10)
- V represents 5
Therefore, XXXV = 30 + 5 = 35
The Roman numeral system is remarkably concise in this case, requiring only four symbols. Imagine representing 35 using only additive principles – it would require seven symbols (IIIII IIIIIII!). The subtractive principle drastically improves efficiency.
The History and Evolution of Roman Numerals
The Roman numeral system originated in ancient Rome, evolving over centuries. Its exact origins are somewhat obscure, with influences possibly stemming from earlier Etruscan numerals. The system wasn't standardized until the late Roman Empire. Various forms and conventions existed before that.
The system's longevity is striking. It was used for centuries in Europe for recording dates, numbering chapters in books, and various other purposes. Even today, it persists in certain contexts, such as clock faces, chapter numbering in books, and occasionally in formal settings to denote order or sequence (e.g., Super Bowl XXXV).
Limitations of the Roman Numeral System
Despite its historical significance and continued use in specific applications, the Roman numeral system has limitations compared to the positional decimal system. These limitations include:
- Lack of a zero: The absence of a zero symbol makes arithmetic operations more challenging.
- No place value: The system lacks the concept of place value, which is fundamental to modern arithmetic. Each symbol's value is inherent, regardless of its position in the number.
- Inefficiency for large numbers: Representing extremely large numbers becomes cumbersome and requires many symbols.
Practical Applications of Roman Numerals Today
While not a primary numbering system in modern society, Roman numerals still hold their place in several specific areas:
- Clock faces: Many analog clocks use Roman numerals for the hours.
- Chapter numbering: Books often use Roman numerals for chapter numbering.
- Outlines and lists: Roman numerals can be used to create organized outlines and lists.
- Copyright dates: Some copyright notices may use Roman numerals.
- Formal settings: Roman numerals may be used in formal settings to indicate ordinal numbers (e.g., King Henry VIII).
- Movie titles and designations: Certain movie titles and sequels might include Roman numerals for numbering.
Beyond XXXV: Exploring Other Roman Numeral Conversions
Understanding how 35 is represented in Roman numerals provides a strong foundation for converting other numbers. Let's explore a few more examples:
- 49: XLIX (50 - 10 + 9)
- 88: LXXXVIII (50 + 10 + 10 + 10 + 8)
- 199: CXCIX (100 + 90 + 9)
- 2024: MMXXIV (1000 + 1000 + 20 + 4)
Mastering Roman Numerals: Tips and Tricks
Learning Roman numerals can be surprisingly enjoyable. Here are a few tips for mastering the system:
- Memorize the basic symbols: Begin by firmly memorizing the seven basic symbols and their values.
- Practice conversions: Regularly practice converting numbers between the decimal and Roman numeral systems. Start with small numbers and gradually increase the complexity.
- Use online resources: There are numerous online tools and converters available to check your work and provide additional practice.
- Understand the additive and subtractive principles: A clear grasp of these two principles is crucial for accurate conversions.
- Break down complex numbers: For larger numbers, break them down into smaller components, making the conversion process more manageable.
Conclusion: The Enduring Legacy of Roman Numerals
While the Roman numeral system may have limitations compared to the modern decimal system, its historical significance and continued presence in specific applications solidify its enduring legacy. Understanding the system, as demonstrated by our exploration of 35 (XXXV), opens a window into the history of mathematics and the fascinating evolution of numerical representation. By grasping the additive and subtractive principles, you can confidently navigate the world of Roman numerals and appreciate their unique character. Whether you're deciphering a clock face, reading a book's chapter numbers, or simply expanding your mathematical knowledge, the Roman numeral system offers a timeless connection to history and a fascinating system of numerical representation.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Much Is 25 Oz In Cups
Mar 26, 2025
-
Does Carbon Have 4 Valence Electrons
Mar 26, 2025
-
How To Calculate Molar Enthalpy Of Combustion
Mar 26, 2025
-
106 Out Of 150 As A Percentage
Mar 26, 2025
-
How Many Electrons Does Oxygen Gain Or Lose
Mar 26, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is 35 In Roman Numerals . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
