How Many Valence Electrons In Cesium
Kalali
Mar 26, 2025 · 5 min read
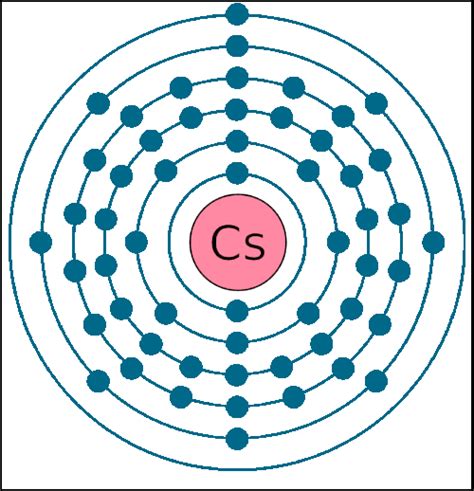
Table of Contents
How Many Valence Electrons Does Cesium Have? A Deep Dive into Alkali Metals
Cesium, a fascinating element with the symbol Cs and atomic number 55, holds a unique place in the periodic table. Understanding its electronic structure, particularly the number of valence electrons, is crucial to grasping its chemical behavior and properties. This article delves deep into the world of cesium, exploring its valence electrons, their significance, and the implications for its reactivity and applications.
Understanding Valence Electrons: The Key to Chemical Behavior
Before focusing specifically on cesium, let's establish a foundational understanding of valence electrons. These are the electrons located in the outermost shell of an atom. They are the primary players in chemical bonding, determining how an atom interacts with other atoms to form molecules and compounds. The number of valence electrons dictates an element's reactivity, its ability to form bonds, and the types of bonds it can form (ionic, covalent, metallic). Elements with similar numbers of valence electrons often exhibit similar chemical properties, a pattern beautifully reflected in the periodic table's organization.
Electron Configuration and Valence Electrons: A Closer Look
The electron configuration of an atom describes how its electrons are distributed among different energy levels and sublevels. This configuration is crucial for determining the number of valence electrons. For example, the electron configuration of cesium (Cs) is [Xe] 6s¹. This notation means that cesium has a core of electrons arranged like xenon (Xe), a noble gas, plus one additional electron in the 6s orbital.
The 6s orbital is the outermost shell, meaning the electron residing in it is the valence electron.
Cesium: A Detailed Look at its Electronic Structure
Cesium belongs to Group 1 of the periodic table, also known as the alkali metals. This group is characterized by elements with a single valence electron. This common feature explains their remarkably similar chemical properties. They are all highly reactive metals, readily losing their single valence electron to form +1 ions. This tendency towards cation formation drives their reactivity and explains many of their observed characteristics.
Cesium's Place in the Periodic Table and its Properties
Cesium's position in the periodic table, specifically in Group 1 and Period 6, directly influences its properties. Its atomic number (55) signifies 55 protons and, in a neutral atom, 55 electrons. The electronic configuration dictates its reactivity and other characteristics. The large atomic radius of cesium, a consequence of its position far down the periodic table, makes it highly reactive. The loosely held single valence electron is easily lost, initiating chemical reactions.
This reactivity is reflected in several ways:
- Low ionization energy: The energy required to remove the valence electron is exceptionally low.
- High electropositivity: Cesium readily loses its electron, becoming a positively charged ion.
- Reactivity with water: Cesium reacts violently with water, releasing hydrogen gas and generating significant heat.
- Reactivity with halogens: Cesium readily forms ionic bonds with halogens (Group 17 elements), forming compounds like cesium chloride (CsCl).
The Significance of Cesium's Single Valence Electron
The single valence electron in cesium is the cornerstone of its chemical behavior. It is this electron that determines cesium's:
- Oxidation state: Cesium almost exclusively exhibits a +1 oxidation state due to the ease with which it loses its single valence electron.
- Bonding behavior: Cesium predominantly forms ionic bonds by donating its valence electron to a more electronegative atom.
- Reactivity: The readiness of cesium to lose its valence electron accounts for its high reactivity with a wide range of substances.
- Applications: Many applications of cesium leverage its unique properties stemming directly from this single valence electron.
Applications of Cesium: Leveraging its Unique Properties
The unique properties of cesium, largely dictated by its single valence electron, lead to its use in several specialized applications. These include:
- Atomic clocks: Cesium's precise atomic transitions make it essential for highly accurate atomic clocks. These clocks are vital in fields requiring ultra-precise timekeeping, such as GPS systems and scientific research. The frequency of the microwave radiation absorbed by cesium atoms is used to define the second in the International System of Units (SI).
- Oil and gas exploration: Cesium formate, a cesium-containing compound, is used in drilling fluids for oil and gas exploration. Its properties help to improve drilling efficiency and reduce environmental impact.
- Medical imaging: While less common, some research explores cesium's potential in medical imaging techniques.
- Photoelectric cells: Cesium's low ionization energy and photoelectric properties make it suitable for use in photoelectric cells, which convert light into electricity.
Conclusion: The Importance of Valence Electrons in Cesium's Chemistry
In summary, cesium possesses one valence electron, located in its outermost 6s orbital. This single electron is the key to understanding cesium's chemistry and its distinctive properties. It explains its high reactivity, its tendency to form ionic compounds, and its role in various specialized applications. From the highly precise atomic clocks that govern modern timekeeping to specialized applications in oil and gas exploration, the impact of cesium's single valence electron extends far beyond its simple atomic structure. A deep understanding of valence electrons is crucial for comprehending the behavior and applications of not just cesium but all elements in the periodic table. Further research into cesium and other alkali metals continues to unveil new insights into their fascinating properties and potential applications. The seemingly simple fact that cesium has one valence electron unlocks a world of complex chemical interactions and technological advancements.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Long Is 21 Cm In Inches
Mar 29, 2025
-
How To Recognize A Redox Reaction
Mar 29, 2025
-
95 Degrees Fahrenheit Converted To Celsius
Mar 29, 2025
-
Whats 2 1 2 As A Decimal
Mar 29, 2025
-
31 Degrees C Is What In F
Mar 29, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Many Valence Electrons In Cesium . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
